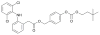Peripheral site acetylcholinesterase inhibitors targeting both inflammation and cholinergic dysfunction
- PMID: 20347302
- PMCID: PMC2864113
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2010.02.102
Peripheral site acetylcholinesterase inhibitors targeting both inflammation and cholinergic dysfunction
Abstract
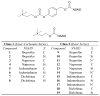
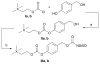
The design and study of two classes of noncompetitive acetylcholinesterase inhibitors (AChEIs) which also function as NSAID prodrugs are reported. The most potent AChEIs disclosed contain an aromatic alkyl-aryl linker between an NSAID and a lipophilic choline mimic and they inhibit acetylcholinesterase (AChE) in the submicromolar range. These agents have the therapeutic potential to dually target inflammation by releasing an NSAID in vivo and activating the cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway via cholinergic up-regulation.
2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Özgüney I. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2008;9:1805–1816. - PubMed
-
- Cannon J. Pharmacology for Chemists. 2. Oxford University Press; New York: Concepts of Pharmacology; pp. 13–17.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Chemical Information