Quantitative reconstitution of mitotic CDK1 activation in somatic cell extracts
- PMID: 20347419
- PMCID: PMC2882237
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2010.02.023
Quantitative reconstitution of mitotic CDK1 activation in somatic cell extracts
Abstract
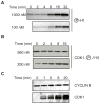
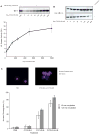
The regulation of mitotic entry in somatic cells differs from embryonic cells, yet it is only for embryonic cells that we have a quantitative understanding of this process. To gain a similar insight into somatic cells, we developed a human cell extract system that recapitulates CDK1 activation and nuclear envelope breakdown in response to mitotic cyclins. As cyclin B concentrations increase, CDK1 activates in a three-stage nonlinear response, creating an ordering of substrate phosphorylations. This response is established by dual regulatory feedback loops involving WEE1/MYT1, which impose a cyclin B threshold, and CDC25, which allows CDK1 to escape the WEE1/MYT1 inhibition. This system also exhibits a complex response to cyclin A. Cyclin A promotes WEE1 phosphorylation to weaken the negative feedback loop and primes mitotic entry through cyclin B. This observation explains the requirement of both cyclin A and cyclin B to initiate mitosis in somatic cells.
(c) 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures





References
-
- Brezak MC, Quaranta M, Mondesert O, Galcera MO, Lavergne O, Alby F, Cazales M, Baldin V, Thurieau C, Harnett J, et al. A novel synthetic inhibitor of CDC25 phosphatases: BN82002. Cancer Res. 2004;64:3320–3325. - PubMed
-
- De Boer L, Oakes V, Beamish H, Giles N, Stevens F, Somodevilla-Torres M, Desouza C, Gabrielli B. Cyclin A/cdk2 coordinates centrosomal and nuclear mitotic events. Oncogene. 2008;27:4261–4268. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

