Esophageal squamous cell dysplasia and delayed differentiation with deletion of krüppel-like factor 4 in murine esophagus
- PMID: 20347813
- PMCID: PMC3265336
- DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2010.03.048
Esophageal squamous cell dysplasia and delayed differentiation with deletion of krüppel-like factor 4 in murine esophagus
Abstract
Background & aims: Krüppel-like factor 4 (Klf; previously known a gut-enriched Krüppel-like factor) is a DNA-binding transcriptional regulator highly expressed in skin and gastrointestinal epithelia, specifically in regions of cellular differentiation. Homozygous null mice for Klf4 die shortly after birth from skin defects, precluding their analysis at later stages. The aim of this study was to analyze the function of Klf4 in keratinocyte biology and epithelial homeostasis in the adult by focusing on the squamous lined esophagus.
Methods: By using the ED-L2 promoter of Epstein-Barr virus to drive Cre, we obtained tissue-specific ablation of Klf4 in the squamous epithelia of the tongue, esophagus, and forestomach.
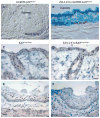
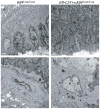
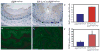
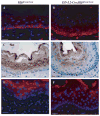
Results: Mice with loss of Klf4 in esophageal epithelia survived to adulthood, bypassing the early lethality. Tissue-specific Klf4 knockout mice had increased basal cell proliferation and a delay in cellular maturation; these mice developed epithelial hypertrophy and subsequent dysplasia by 6 months of age. Moreover, loss of Klf4 in vivo was associated with increased expression of the pro-proliferative Klf5, and Klf4 down-regulated Klf5 both transcriptionally and posttranscriptionally. By using gene expression profiling, we also showed decreased expression of critical late-stage differentiation factors and identified alterations of several genes important in cellular differentiation.
Conclusions: Klf4 is essential for squamous epithelial differentiation in vivo and interacts with Klf5 to maintain normal epithelial homeostasis.
Copyright 2010 AGA Institute. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Stappenbeck TS, Wong MH, Saam JR, et al. Notes from some crypt watchers: regulation of renewal in the mouse intestinal epithelium. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1998;10:702–9. - PubMed
-
- Squier CA, Kremer MJ. Biology of oral mucosa and esophagus. J Natl Cancer Inst Monogr. 2001:7–15. - PubMed
-
- Seery JP. Stem cells of the oesophageal epithelium. J Cell Sci. 2002;115:1783–9. - PubMed
-
- Katz JP, Kaestner KH. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of carcinogenesis. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 2002;31:379–94. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

