Acquired infection with Toxoplasma gondii in adult mice results in sensorimotor deficits but normal cognitive behavior despite widespread brain pathology
- PMID: 20348009
- PMCID: PMC2891993
- DOI: 10.1016/j.micinf.2010.03.009
Acquired infection with Toxoplasma gondii in adult mice results in sensorimotor deficits but normal cognitive behavior despite widespread brain pathology
Abstract
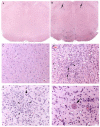
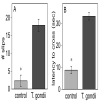
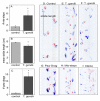
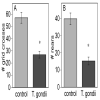
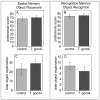
Toxoplasma gondii is a ubiquitous intracellular parasite which chronically infects 30-50% of the human population. While acquired infection is primarily asymptomatic several studies have suggested that such infections may contribute to neurological and psychiatric symptoms. Previous studies in rodents have demonstrated that T. gondii infection does not just kill its host, but alters the behavioral repertoire of an infected animal, making it more likely that predation with occur completing the parasite life cycle. The aim of the present study was to evaluate the behavioral changes in C57BL/6 mice chronically infected with the avirulent T. gondii (ME49, a Type II strain), in a comprehensive test battery. Infected mice demonstrated profound and widespread brain pathology, motor coordination and sensory deficits. In contrast, cognitive function, anxiety levels, social behavior and the motivation to explore novel objects were normal. The observed changes in behavior did not represent "gross" brain damage or dysfunction and were not due to targeted destruction of specific areas of the brain. Such changes point out the subtle interaction of this parasite with its intermediate hosts and are consistent with ideas about increased predation being an outcome of infection.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Chronic Toxoplasma infection modifies the structure and the risk of host behavior.PLoS One. 2012;7(3):e32489. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0032489. Epub 2012 Mar 14. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22431975 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide comparative analysis revealed significant transcriptome changes in mice after Toxoplasma gondii infection.Parasit Vectors. 2013 Jun 4;6:161. doi: 10.1186/1756-3305-6-161. Parasit Vectors. 2013. PMID: 23734932 Free PMC article.
-
[Toxoplasma gondii: a potential role in the genesis of psychiatric disorders].Encephale. 2013 Feb;39(1):38-43. doi: 10.1016/j.encep.2012.06.014. Epub 2012 Aug 21. Encephale. 2013. PMID: 23095600 Review. French.
-
Toxoplasma gondii superinfection and virulence during secondary infection correlate with the exact ROP5/ROP18 allelic combination.mBio. 2015 Feb 24;6(2):e02280. doi: 10.1128/mBio.02280-14. mBio. 2015. PMID: 25714710 Free PMC article.
-
Toxoplasma gondii infection and behaviour - location, location, location?J Exp Biol. 2013 Jan 1;216(Pt 1):113-9. doi: 10.1242/jeb.074153. J Exp Biol. 2013. PMID: 23225873 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of Toxoplasma gondii infection on anxiety, depression and ghrelin level in male rats.J Parasit Dis. 2016 Sep;40(3):688-93. doi: 10.1007/s12639-014-0561-0. Epub 2014 Sep 11. J Parasit Dis. 2016. PMID: 27605768 Free PMC article.
-
Passage of parasites across the blood-brain barrier.Virulence. 2012 Mar-Apr;3(2):202-12. doi: 10.4161/viru.19178. Epub 2012 Mar 1. Virulence. 2012. PMID: 22460639 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Toxoplasma gondii infection as a risk factor for osteoporosis: a case-control study.Parasit Vectors. 2022 Apr 27;15(1):151. doi: 10.1186/s13071-022-05257-z. Parasit Vectors. 2022. PMID: 35477558 Free PMC article.
-
Toxoplasma gondii IgG Serointensity Is Positively Associated With Frailty.J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2024 Mar 1;79(3):glad228. doi: 10.1093/gerona/glad228. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 37939652 Free PMC article.
-
Toxoplasma gondii Infection in Mice Impairs Long-Term Fear Memory Consolidation through Dysfunction of the Cortex and Amygdala.Infect Immun. 2016 Sep 19;84(10):2861-70. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00217-16. Print 2016 Oct. Infect Immun. 2016. PMID: 27456832 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dubey JP. History of the discovery of the life cycle of Toxoplasma gondii. International Journal for Parasitology. 2009;39:877–882. - PubMed
-
- Henriquez SA, Brett R, Alexander J, Pratt J, Roberts CW. Neuropsychiatric disease and Toxoplasma gondii infection. Neuroimmunomodulation. 2009;16:122–133. - PubMed
-
- Yolken RH, Dickerson FB, Torrey E. Fuller. Toxoplasma and schizophrenia. Parasite Immunol. 2009;31:706–715. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

