LMP1 regulates periodontal ligament progenitor cell proliferation and differentiation
- PMID: 20348040
- PMCID: PMC2891403
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bone.2010.03.013
LMP1 regulates periodontal ligament progenitor cell proliferation and differentiation
Abstract
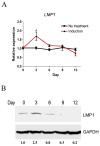
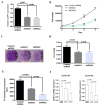
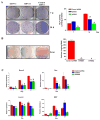
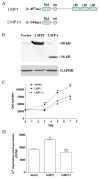
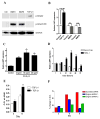
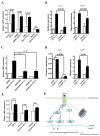
LMP1 is an intracellular scaffold protein that contains a PDZ domain and three LIM domains. LMP1 has multiple functions including regulating mesenchymal stem cell (MSC) osteogenesis. Gene delivery of LMP1 induces bone formation in vivo in heterotopic and orthotopic sites. However, little is known about the physiological function and gene regulatory mechanisms of LMP1 in MSCs at the molecular level. Periodontal ligament (PDL) cells are a unique progenitor cell population that can differentiate into multiple cell types, including osteoblasts, adipocytes, or chondrocytes. This study sought to determine the physiological function and gene regulatory mechanisms of LMP1 in PDL cells at the molecular level. We show that LMP1 is upregulated in early stage of PDL cell osteogenic differentiation. Stable gene knockdown of LMP1 by shRNA inhibits DNA synthesis and corresponding cell proliferation in PDL cells, and further leads to decreased mineralization in vitro. Overexpression of LMP1 increases cell proliferation, and PDZ and ww-interacting domains are not sufficient to mediate this effect. Further, we found that in PDL cells, LMP1 is a downstream target gene of TGF-beta1 that is an early signal critical in preosteoblast proliferation and differentiation. TGF-beta1 stimulates PDL cell proliferation, however, this effect is compromised when LMP1 is knocked down. We further identified that the activation of TAK1-JNK/p38 kinase cascade is involved in the LMP1 gene regulation by TGF-beta1. We conclude that LMP1 is a downstream gene of TGF-beta1, involved in PDL cell proliferation. Our findings advance the understanding of the physiological function of LMP1 and define a regulatory mechanism of LMP1 in PDL progenitor cells and other MSCs.
2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of TGF-β1 on the proliferation and differentiation of human periodontal ligament cells and a human periodontal ligament stem/progenitor cell line.Cell Tissue Res. 2010 Nov;342(2):233-42. doi: 10.1007/s00441-010-1037-x. Epub 2010 Oct 8. Cell Tissue Res. 2010. PMID: 20931341
-
TGF-β-operated growth inhibition and translineage commitment into smooth muscle cells of periodontal ligament-derived endothelial progenitor cells through Smad- and p38 MAPK-dependent signals.Int J Biol Sci. 2012;8(7):1062-74. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.4488. Epub 2012 Aug 22. Int J Biol Sci. 2012. PMID: 22949889 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancing effects of myricetin on the osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells via BMP-2/Smad and ERK/JNK/p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway.Eur J Pharmacol. 2018 Sep 5;834:84-91. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2018.07.012. Epub 2018 Jul 20. Eur J Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 30012495
-
Endoglin is involved in BMP-2-induced osteogenic differentiation of periodontal ligament cells through a pathway independent of Smad-1/5/8 phosphorylation.J Cell Physiol. 2010 Feb;222(2):465-73. doi: 10.1002/jcp.21968. J Cell Physiol. 2010. PMID: 19918795
-
The many faces of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase in progenitor/stem cell differentiation.Biochem J. 2012 Jul 1;445(1):1-10. doi: 10.1042/BJ20120401. Biochem J. 2012. PMID: 22702973 Review.
Cited by
-
LIM Mineralization Protein-1 Enhances the Committed Differentiation of Dental Pulp Stem Cells through the ERK1/2 and p38 MAPK Pathways and BMP Signaling.Int J Med Sci. 2022 Jul 18;19(8):1307-1319. doi: 10.7150/ijms.70411. eCollection 2022. Int J Med Sci. 2022. PMID: 35928717 Free PMC article.
-
Lim mineralization protein 3 induces the osteogenic differentiation of human amniotic fluid stromal cells through Kruppel-like factor-4 downregulation and further bone-specific gene expression.J Biomed Biotechnol. 2012;2012:813894. doi: 10.1155/2012/813894. Epub 2012 Oct 2. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2012. PMID: 23097599 Free PMC article.
-
The unexpected versatility of ALP/Enigma family proteins.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Dec 1;10:963608. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.963608. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 36531944 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biologic Agents for Periodontal Regeneration and Implant Site Development.Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:957518. doi: 10.1155/2015/957518. Epub 2015 Oct 5. Biomed Res Int. 2015. PMID: 26509173 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phenotypic Modulation of Smooth Muscle Cells in Atherosclerosis Is Associated With Downregulation of LMOD1, SYNPO2, PDLIM7, PLN, and SYNM.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2016 Sep;36(9):1947-61. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.116.307893. Epub 2016 Jul 28. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2016. PMID: 27470516 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Durick K, Wu RY, Gill GN, Taylor SS. Mitogenic signaling by Ret/ptc2 requires association with enigma via a LIM domain. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:12691–4. - PubMed
-
- Boden SD, Liu Y, Hair GA, Helms JA, Hu D, Racine M, Nanes MS, Titus L. LMP-1, a LIM-domain protein, mediates BMP-6 effects on bone formation. Endocrinology. 1998;139:5125–34. - PubMed
-
- Boden SD, Titus L, Hair G, Liu Y, Viggeswarapu M, Nanes MS, Baranowski C. Lumbar spine fusion by local gene therapy with a cDNA encoding a novel osteoinductive protein (LMP-1) Spine. 1998;23:2486–92. - PubMed
-
- Liu Y, Hair GA, Boden SD, Viggeswarapu M, Titus L. Overexpressed LIM mineralization proteins do not require LIM domains to induce bone. J Bone Miner Res. 2002;17:406–14. - PubMed
-
- Pola E, Gao W, Zhou Y, Pola R, Lattanzi W, Sfeir C, Gambotto A, Robbins PD. Efficient bone formation by gene transfer of human LIM mineralization protein-3. Gene Ther. 2004;11:683–93. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

