Mechanotransduction by GEF-H1 as a novel mechanism of ventilator-induced vascular endothelial permeability
- PMID: 20348280
- PMCID: PMC2886610
- DOI: 10.1152/ajplung.00263.2009
Mechanotransduction by GEF-H1 as a novel mechanism of ventilator-induced vascular endothelial permeability
Abstract
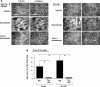
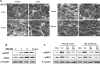
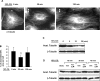
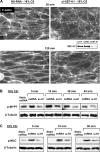
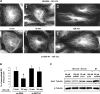
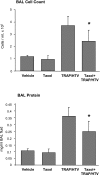
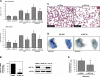
Pathological lung overdistention associated with mechanical ventilation at high tidal volumes (ventilator-induced lung injury; VILI) compromises endothelial cell (EC) barrier leading to development of pulmonary edema and increased morbidity and mortality. We have previously shown involvement of microtubule (MT)-associated Rho-specific guanine nucleotide exchange factor GEF-H1 in the agonist-induced regulation of EC permeability. Using an in vitro model of human pulmonary EC exposed to VILI-relevant magnitude of cyclic stretch (18% CS) we tested a hypothesis that CS-induced alterations in MT dynamics contribute to the activation of Rho-dependent signaling via GEF-H1 and mediate early EC response to pathological mechanical stretch. Acute CS (30 min) induced disassembly of MT network, cell reorientation, and activation of Rho pathway, which was prevented by MT stabilizer taxol. siRNA-based GEF-H1 knockdown suppressed CS-induced disassembly of MT network, abolished Rho signaling, and attenuated CS-induced stress fiber formation and EC realignment compared with nonspecific RNA controls. Depletion of GEF-H1 in the murine two-hit model of VILI attenuated vascular leak induced by lung ventilation at high tidal volume and thrombin-derived peptide TRAP6. These data show for the first time the critical involvement of microtubules and microtubule-associated GEF-H1 in lung vascular endothelial barrier dysfunction induced by pathological mechanical strain.
Figures
References
-
- The Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Network Ventilation with lower tidal volumes as compared with traditional tidal volumes for acute lung injury and the acute respiratory distress syndrome. N Engl J Med 342: 1301–1308, 2000 - PubMed
-
- Belperio JA, Keane MP, Lynch JP, 3rd, Strieter RM. The role of cytokines during the pathogenesis of ventilator-associated and ventilator-induced lung injury. Semin Respir Crit Care Med 27: 350–364, 2006 - PubMed
-
- Bershadsky AD, Balaban NQ, Geiger B. Adhesion-dependent cell mechanosensitivity. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 19: 677–695, 2003 - PubMed
-
- Birkenfeld J, Nalbant P, Yoon SH, Bokoch GM. Cellular functions of GEF-H1, a microtubule-regulated Rho-GEF: is altered GEF-H1 activity a crucial determinant of disease pathogenesis? Trends Cell Biol 18: 210–219, 2008 - PubMed
-
- Birukov KG, Bochkov VN, Birukova AA, Kawkitinarong K, Rios A, Leitner A, Verin AD, Bokoch GM, Leitinger N, Garcia JG. Epoxycyclopentenone-containing oxidized phospholipids restore endothelial barrier function via Cdc42 and Rac. Circ Res 95: 892–901, 2004 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

