T helper type 1 and 17 cells determine efficacy of interferon-beta in multiple sclerosis and experimental encephalomyelitis
- PMID: 20348925
- PMCID: PMC3042885
- DOI: 10.1038/nm.2110
T helper type 1 and 17 cells determine efficacy of interferon-beta in multiple sclerosis and experimental encephalomyelitis
Abstract
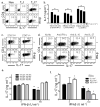
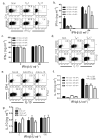
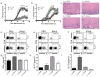
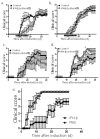
Interferon-beta (IFN-beta) is the major treatment for multiple sclerosis. However, this treatment is not always effective. Here we have found congruence in outcome between responses to IFN-beta in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) and relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis (RRMS). IFN-beta was effective in reducing EAE symptoms induced by T helper type 1 (T(H)1) cells but exacerbated disease induced by T(H)17 cells. Effective treatment in T(H)1-induced EAE correlated with increased interleukin-10 (IL-10) production by splenocytes. In T(H)17-induced disease, the amount of IL-10 was unaltered by treatment, although, unexpectedly, IFN-beta treatment still reduced IL-17 production without benefit. Both inhibition of IL-17 and induction of IL-10 depended on IFN-gamma. In the absence of IFN-gamma signaling, IFN-beta therapy was ineffective in EAE. In RRMS patients, IFN-beta nonresponders had higher IL-17F concentrations in serum compared to responders. Nonresponders had worse disease with more steroid usage and more relapses than did responders. Hence, IFN-beta is proinflammatory in T(H)17-induced EAE. Moreover, a high IL-17F concentration in the serum of people with RRMS is associated with nonresponsiveness to therapy with IFN-beta.
Figures

Comment in
-
Molecular oracles for multiple sclerosis therapy.Nat Med. 2010 Apr;16(4):376-7. doi: 10.1038/nm0410-376. Nat Med. 2010. PMID: 20376043 No abstract available.
References
-
- Arnason BG. Immunologic therapy of multiple sclerosis. Annu Rev Med. 1999;50:291–302. - PubMed
-
- Wang AG, Lin YC, Wang SJ, Tsai CP, Yen MY. Early relapse in multiple sclerosis-associated optic neuritis following the use of interferon beta-1a in Chinese patients. Jpn J Ophthalmol. 2006;50:537–42. - PubMed
-
- Benveniste EN, Qin H. Type I interferons as anti-inflammatory mediators. Sci STKE. 2007;2007:pe70. - PubMed
-
- Prinz M, et al. Distinct and Nonredundant In Vivo Functions of IFNAR on Myeloid Cells Limit Autoimmunity in the Central Nervous System. Immunity. 2008 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

