Membrane-bound mucins: the mechanistic basis for alterations in the growth and survival of cancer cells
- PMID: 20348949
- PMCID: PMC2879972
- DOI: 10.1038/onc.2010.87
Membrane-bound mucins: the mechanistic basis for alterations in the growth and survival of cancer cells
Abstract
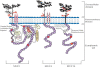
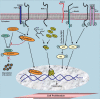
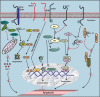
Mucins (MUC) are high molecular weight O-linked glycoproteins whose primary functions are to hydrate, protect, and lubricate the epithelial luminal surfaces of the ducts within the human body. The MUC family is comprised of large secreted gel forming and transmembrane (TM) mucins. MUC1, MUC4, and MUC16 are the well-characterized TM mucins and have been shown to be aberrantly overexpressed in various malignancies including cystic fibrosis, asthma, and cancer. Recent studies have uncovered the unique roles of these mucins in the pathogenesis of cancer. These mucins possess specific domains that can make complex associations with various signaling pathways, impacting cell survival through alterations of cell growth, proliferation, death, and autophagy. The cytoplasmic domain of MUC1 serves as a scaffold for interaction with various signaling proteins. On the other hand, MUC4 mediates its effect by stabilizing and enhancing the activity of growth factor receptor ErbB2. MUC16, previously known as CA125, is a well-known serum marker for the diagnosis of ovarian cancer and has a key role in stimulation and dissemination of ovarian cancer cells by interacting with mesothelin and galectin. Therefore, herein we discuss the function and divergent mechanisms of MUC1, MUC4, and MUC16 in carcinogenesis in the context of alteration in cell growth and survival.
Figures

References
-
- Andrianifahanana M, Moniaux N, Schmied BM, Ringel J, Friess H, Hollingsworth MA, et al. Mucin (MUC) gene expression in human pancreatic adenocarcinoma and chronic pancreatitis: a potential role of MUC4 as a tumor marker of diagnostic significance. Clin Cancer Res. 2001;7:4033–4040. - PubMed
-
- Arango ME, Li P, Komatsu M, Montes C, Carraway CA, Carraway KL. Production and localization of Muc4/sialomucin complex and its receptor tyrosine kinase ErbB2 in the rat lacrimal gland. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2001;42:2749–2756. - PubMed
-
- Argueso P, Spurr-Michaud S, Russo CL, Tisdale A, Gipson IK. MUC16 mucin is expressed by the human ocular surface epithelia and carries the H185 carbohydrate epitope. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2003;44:2487–2495. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

