Sensory and vascular changes in a rat monoarthritis model: prophylactic and therapeutic effects of meloxicam
- PMID: 20349327
- PMCID: PMC5132625
- DOI: 10.1007/s00011-010-0179-3
Sensory and vascular changes in a rat monoarthritis model: prophylactic and therapeutic effects of meloxicam
Abstract
Objective and design: The objective of this study was to determine the ability of meloxicam prophylaxis and therapy to blunt the effect of complete Freund's adjuvant (CFA) induced monoarthritis.
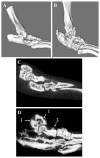
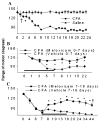
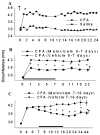
Materials and methods: First the validity of this animal model was established by examining joint changes at multiple levels after injecting CFA into the tibio-tarsal joint. Next, meloxicam (5 mg/kg) or vehicle was administered on days 0-7 (prophylactic) and on days 7-16 (therapeutic) in separate groups of animals.
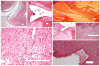
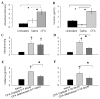
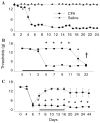
Results: The CFA-injected joint demonstrated hallmark histological and structural changes such as pannus formation, bone remodeling, cartilage erosion and immune cell infiltration. Both prophylactic and therapeutic treatment with meloxicam effectively reduced swelling (ankle circumference), oedema and extravasation of Evans blue dye in the affected joint. Moreover, meloxicam reduced loss in range of motion and also reduced mechanical stimulus evoked pain scores. Notably, these effects persisted after discontinuing drug treatment.
Conclusion: The present study provides a unique comparison of prophylactic versus therapeutic effects of meloxicam in the CFA-induced model of monoarthritis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of buprenorphine on model development in an adjuvant-induced monoarthritis rat model.PLoS One. 2022 Jan 13;17(1):e0260356. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0260356. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35025864 Free PMC article.
-
Non-steroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs Attenuate Hyperalgesia and Block Upregulation of Trigeminal Ganglionic Sodium Channel 1.7 after Induction of Temporomandibular Joint Inflammation in Rats.Chin J Dent Res. 2016 Mar;19(1):35-42. doi: 10.3290/j.cjdr.a35695. Chin J Dent Res. 2016. PMID: 26981605
-
Meloxicam: a potent inhibitor of adjuvant arthritis in the Lewis rat.Inflamm Res. 1995 Dec;44(12):548-55. doi: 10.1007/BF01757360. Inflamm Res. 1995. PMID: 8788236
-
Meloxicam in rheumatoid arthritis.Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2005 Dec;1(4):739-51. doi: 10.1517/17425255.1.4.739. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2005. PMID: 16863437 Review.
-
Relative value of the NSAIDs, including COX-2 inhibitors and meloxicam.J Manag Care Pharm. 2006 Apr;12(3):265-8. doi: 10.18553/jmcp.2006.12.3.265. J Manag Care Pharm. 2006. PMID: 16623613 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Benefits of electroacupuncture and a swimming association when compared with isolated protocols in an osteoarthritis model.J Tradit Complement Med. 2021 Nov 23;12(4):375-383. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcme.2021.11.002. eCollection 2022 Jul. J Tradit Complement Med. 2021. PMID: 35747360 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of buprenorphine on model development in an adjuvant-induced monoarthritis rat model.PLoS One. 2022 Jan 13;17(1):e0260356. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0260356. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35025864 Free PMC article.
-
Antinociceptive effects of fentanyl and nonopioid drugs in methocinnamox-treated rats.Drug Alcohol Depend. 2024 Jul 1;260:111320. doi: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2024.111320. Epub 2024 Apr 29. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2024. PMID: 38723374 Free PMC article.
-
Cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor celecoxib attenuates joint contracture following immobilization in rat knees.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2016 Oct 24;17(1):446. doi: 10.1186/s12891-016-1303-5. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2016. PMID: 27776498 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel Diabetic Arthritic Model in Rats Induced by Streptozotocin, High-Fat Diet, and Complete Freund's Adjuvant.Orthop Res Rev. 2024 Jun 11;16:163-170. doi: 10.2147/ORR.S457848. eCollection 2024. Orthop Res Rev. 2024. PMID: 38882468 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kvien TK. Epidemiology and burden of illness of rheumatoid arthritis. Pharmacoeconomics. 2004;22(2 Suppl 1):1–12. - PubMed
-
- Sprangers MA, de Regt EB, Andries F, van Agt HM, Bijl RV, de Boer JB, et al. Which chronic conditions are associated with better or poorer quality of life? J Clin Epidemiol. 2000;53(9):895–907. - PubMed
-
- Testa MA, Simonson DC. Assessment of quality-of-life outcomes. N Engl J Med. 1996;334(13):835–40. - PubMed
-
- Uhlig T, Loge JH, Kristiansen IS, Kvien TK. Quantification of reduced health-related quality of life in patients with rheumatoid arthritis compared to the general population. J Rheumatol. 2007;34(6):1241–7. - PubMed
-
- Badley EM, Webster GK, Rasooly I. The impact of musculo-skeletal disorders in the population: are they just aches and pains? Findings from the 1990 Ontario Health Survey. J Rheumatol. 1995;22(4):733–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

