Chronic kidney disease and cancer: a troubling connection
- PMID: 20349418
- PMCID: PMC4823382
Chronic kidney disease and cancer: a troubling connection
Abstract
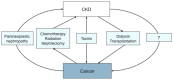
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) and cancer are connected in a number of ways in both directions: cancer can cause CKD either directly or indirectly through the adverse effects of therapies; CKD may, conversely, be a risk factor for cancer; and both may be associated because they share common risk factors, often toxins. In this review, we briefly address the issue of paraneoplastic nephropathies as well as that of toxin-related cancers and CKD, including analgesic and aristolochic acid nephropathies. We then focus on the links between the various stages of CKD and cancer incidence, and critically examine major epidemiologic surveys in the field. Compared with the general population, kidney transplant recipients have a threefold to fourfold increase in overall cancer risk, and relative risks higher than 3 for about 20 specific tumors, most, but not all, of which are known or suspected to be caused by viral agents. After dialysis, cancer risk increases 10% to 80% according to studies, with relative risks significantly higher than in the general population, for about 10 cancer sites. There is emerging evidence for an excess risk of cancer in patients in early CKD stages.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest : none
Figures
References
-
- K/DOQI clinical practice guidelines for chronic kidney disease: evaluation, classification, and stratification. Am J Kidney Dis. 2002;39(Suppl 1):S1–266. - PubMed
-
- Levey AS, Atkins R, Coresh J, et al. Chronic kidney disease as a global public health problem: approaches and initiatives - a position statement from Kidney Disease Improving Global Outcomes. Kidney Int. 2007;72:247–259. - PubMed
-
- Ronco PM. Paraneoplastic glomerulopathies: new insights into an old entity. Kidney Int. 1999;56:355–377. - PubMed
-
- Audard V, Larousserie F, Grimbert P, et al. Minimal change nephrotic syndrome and classical Hodgkin’s lymphoma: report of 21 cases and review of the literature. Kidney Int. 2006;69:2251–2260. - PubMed