Effects of sevoflurane preconditioning and postconditioning on rat myocardial stunning in ischemic reperfusion injury
- PMID: 20349523
- PMCID: PMC2852543
- DOI: 10.1631/jzus.B0900390
Effects of sevoflurane preconditioning and postconditioning on rat myocardial stunning in ischemic reperfusion injury
Abstract
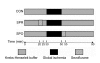
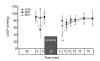
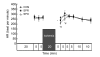
Ischemic preconditioning and postconditioning distinctly attenuate ventricular arrhythmia after ischemia without affecting the severity of myocardial stunning. Therefore, we report the effects of sevoflurane preconditioning and postconditioning on stunned myocardium in isolated rat hearts. Isolated rat hearts were underwent 20 min of global ischemia and 40 min of reperfusion. After an equilibration period (20 min), the hearts in the preconditioning group were exposed to sevoflurane for 5 min and next washout for 5 min before ischemia. Hearts in the sevoflurane postconditioning group underwent equilibration and ischemia, followed immediately by sevoflurane exposure for the first 5 min of reperfusion. The control group received no treatment before and after ischemia. Left ventricular pressure, heart rate, coronary flow, electrocardiogram, and tissue histology were measured as variables of ventricular function and cellular injury, respectively. There was no significant difference in the duration of reperfusion ventricular arrhythmias between control and sevoflurane preconditioning group (P=0.195). The duration of reperfusion ventricular arrhythmias in the sevoflurane postconditioning group was significantly shorter than that in the other two groups (P<0.05). +/-(dP/dt)(max) in the sevoflurane preconditioning group at 5, 10, 15, 20, and 30 min after reperfusion was significantly higher than that in the control group (P<0.05), and there were no significant differences at 40 min after reperfusion among the three groups (P>0.05). As expected, for a 20-min general ischemia, infarct size in heart slices determined by 2,3,5-triphenyltetrazolium chloride staining among the groups was not obvious. Sevoflurane postconditioning reduces reperfusion arrhythmias without affecting the severity of myocardial stunning. In contrast, sevoflurane preconditioning has no beneficial effects on reperfusion arrhythmias, but it is in favor of improving ventricular function and recovering myocardial stunning. Sevoflurane preconditioning and postconditioning may be useful for correcting the stunned myocardium.
Figures
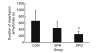


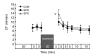
References
-
- Bolli R, Marban E. Molecular and cellular mechanisms of myocardial stunning. Physiol Rev. 1999;79(2):609–634. - PubMed
-
- Bouwman RA, Salic K, Padding FG, Eringa EC, van Beek-Harmsen BJ, Matsuda T, Baba A, Musters RJ, Paulus WJ, de Lange JJ, et al. Cardioprotection via activation of protein kinase C-delta depends on modulation of the reverse mode of the Na+/Ca2+ exchanger. Circulation. 2006;114(1Suppl.):I226–I232. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.105.000570. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Braunwald E, Kloner RA. The stunned myocardium: prolonged, postischemic ventricular dysfunction. Circulation. 1982;66(6):1146–1149. - PubMed
-
- Chiari PC, Bienengraeber MW, Pagel PS, Krolikowski JG, Kersten JR, Warltier DC. Isoflurane protects against myocardial infarction during early reperfusion by activation of phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase signal transduction: evidence for anesthetic-induced postconditioning in rabbits. Anesthesiology. 2005;102(1):102–109. doi: 10.1097/00000542-200501000-00018. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

