Placenta growth factor (PlGF), a novel inducer of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1) in sickle cell disease (SCD)
- PMID: 20351105
- PMCID: PMC2878021
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.101691
Placenta growth factor (PlGF), a novel inducer of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1) in sickle cell disease (SCD)
Abstract
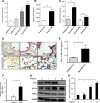
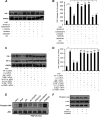
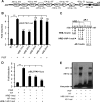
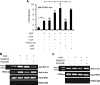
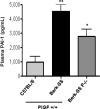
Sickle cell disease (SCD) is characterized by a prothrombotic state. Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1) is known to modulate fibrinolysis, lung injury/fibrosis, and angiogenesis. However, its role in SCD is less understood, and the molecular mechanisms underlying increased PAI-1 are unknown. Herein, we show a novel link between PAI-1 and sickle erythropoiesis. Plasma PAI-1 levels were high in SCD patients at steady state and in two humanized sickle mouse models, with increased PAI-1 immunolabeling in sickle mouse lung, bronchial epithelial cells, alveolar macrophages, and pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells. Placenta growth factor (PlGF), released at high levels by sickle erythroblasts, induced PAI-1 expression in primary human pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells and monocytes through activation of c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK), NADPH oxidase, and hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha (HIF-1alpha). Analysis of the human PAI-1 promoter revealed this induction was mediated by hypoxia-response element (HRE)-1, HRE-2, and distal activator protein (AP-1) sites. We also identify the involvement of c-Jun, c-Jun/c-Fos, and JunD, but not JunB, in binding with AP-1 sites of the PAI-1 promoter upon PlGF induction. Consistent with these findings, levels of PAI-1 were low in PlGF knock-out mice and sickle-PlGF knock-out mice; overexpression of PlGF in normal mice increased circulating PAI-1. In conclusion, we identify a novel mechanism of PAI-1 elevation in SCD.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-α-mediated transcription of miR-301a and miR-454 and their host gene SKA2 regulates endothelin-1 and PAI-1 expression in sickle cell disease.Biosci Rep. 2015 Oct 12;35(6):e00275. doi: 10.1042/BSR20150190. Biosci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26460070 Free PMC article.
-
Erythropoietin-mediated expression of placenta growth factor is regulated via activation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α and post-transcriptionally by miR-214 in sickle cell disease.Biochem J. 2015 Jun 15;468(3):409-23. doi: 10.1042/BJ20141138. Epub 2015 Apr 16. Biochem J. 2015. PMID: 25876995 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of miR-30c and miR-301a in immediate induction of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 by placental growth factor in human pulmonary endothelial cells.Biochem J. 2011 Mar 15;434(3):473-82. doi: 10.1042/BJ20101585. Biochem J. 2011. PMID: 21175428 Free PMC article.
-
Placenta growth factor induces 5-lipoxygenase-activating protein to increase leukotriene formation in sickle cell disease.Blood. 2009 Jan 29;113(5):1129-38. doi: 10.1182/blood-2008-07-169821. Epub 2008 Oct 22. Blood. 2009. PMID: 18945963 Free PMC article.
-
Placenta growth factor mediated gene regulation in sickle cell disease.Blood Rev. 2018 Jan;32(1):61-70. doi: 10.1016/j.blre.2017.08.008. Epub 2017 Aug 16. Blood Rev. 2018. PMID: 28823762 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Inflammation and autoimmunity are interrelated in patients with sickle cell disease at a steady-state condition: implications for vaso-occlusive crisis, pain, and sensory sensitivity.Front Immunol. 2024 Feb 1;15:1288187. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1288187. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38361924 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA 648 Targets ET-1 mRNA and is cotranscriptionally regulated with MICAL3 by PAX5.Mol Cell Biol. 2015 Feb;35(3):514-28. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01199-14. Epub 2014 Nov 17. Mol Cell Biol. 2015. PMID: 25403488 Free PMC article.
-
Beyond the definitions of the phenotypic complications of sickle cell disease: an update on management.ScientificWorldJournal. 2012;2012:949535. doi: 10.1100/2012/949535. Epub 2012 Aug 1. ScientificWorldJournal. 2012. PMID: 22924029 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inflammation in sickle cell disease.Clin Hemorheol Microcirc. 2018;68(2-3):263-299. doi: 10.3233/CH-189012. Clin Hemorheol Microcirc. 2018. PMID: 29614637 Free PMC article.
-
Heme-bound iron activates placenta growth factor in erythroid cells via erythroid Krüppel-like factor.Blood. 2014 Aug 7;124(6):946-54. doi: 10.1182/blood-2013-11-539718. Epub 2014 Jun 10. Blood. 2014. PMID: 24916507 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Francis R. B., Jr., Johnson C. S. (1991) Blood 77, 1405–1414 - PubMed
-
- Gladwin M. T., Sachdev V., Jison M. L., Shizukuda Y., Plehn J. F., Minter K., Brown B., Coles W. A., Nichols J. S., Ernst I., Hunter L. A., Blackwelder W. C., Schechter A. N., Rodgers G. P., Castro O., Ognibene F. P. (2004) N. Engl. J. Med. 350, 886–895 - PubMed
-
- Bunn H. F. (1997) N. Engl. J. Med. 337, 762–769 - PubMed
-
- Key N. S., Slungaard A., Dandelet L., Nelson S. C., Moertel C., Styles L. A., Kuypers F. A., Bach R. R. (1998) Blood 91, 4216–4223 - PubMed
-
- Ataga K. I., Moore C. G., Hillery C. A., Jones S., Whinna H. C., Strayhorn D., Sohier C., Hinderliter A., Parise L. V., Orringer E. P. (2008) Haematologica. 93, 20–26 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

