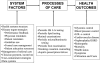
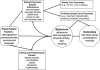
Health systems, patients factors, and quality of care for diabetes: a synthesis of findings from the TRIAD study
- PMID: 20351230
- PMCID: PMC2845056
- DOI: 10.2337/dc09-1802
Health systems, patients factors, and quality of care for diabetes: a synthesis of findings from the TRIAD study
Figures

References
-
- Narayan KM, Boyle JP, Geiss LS, Saaddine JB, Thompson TJ. Impact of recent increase in incidence on future diabetes burden: U.S., 2005–2050. Diabetes Care 2006;29:2114–2116 - PubMed
-
- Selby JV, Ray GT, Zhang D, Colby CJ. Excess costs of medical care for patients with diabetes in a managed care population. Diabetes Care 1997;20:1396–1402 - PubMed
-
- The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Research Group. The effect of intensive treatment of diabetes on the development and progression of long-term complications in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med 1993;329:977–986 - PubMed
-
- Pyŏrälä K, Pedersen TR, Kjekshus J, Faergeman O, Olsson AG, Thorgeirsson G. Cholesterol lowering with simvastatin improves prognosis of diabetic patients with coronary heart disease: a subgroup analysis of the Scandinavian Simvastatin Survival Study. Diabetes Care 1997;20:614–620 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

