Active galactic nucleus feedback in clusters of galaxies
- PMID: 20351250
- PMCID: PMC2867695
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0913904107
Active galactic nucleus feedback in clusters of galaxies
Abstract
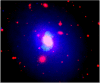
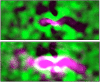
Observations made during the last ten years with the Chandra X-ray Observatory have shed much light on the cooling gas in the centers of clusters of galaxies and the role of active galactic nucleus (AGN) heating. Cooling of the hot intracluster medium in cluster centers can feed the supermassive black holes found in the nuclei of the dominant cluster galaxies leading to AGN outbursts which can reheat the gas, suppressing cooling and large amounts of star formation. AGN heating can come in the form of shocks, buoyantly rising bubbles that have been inflated by radio lobes, and the dissipation of sound waves.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Croton DJ, et al. The many lives of active galactic nuclei: Cooling flows, black holes and the luminosities and colours of galaxies. Mon Not R Astron Soc. 2006;365:11–28.
-
- Allen SW, Schmidt RW, Ebeling H, Fabian AC, van Speybroeck L. Constraints on dark energy from Chandra observations of the largest relaxed galaxy clusters. Mon Not R Astron Soc. 2004;353:457–467.
-
- Fabian AC. Cooling flows in clusters of galaxies. Annu Rev Astron Astr. 1994;32:277–318.
-
- White DA, Jones C, Forman W. An investigation of cooling flows and general cluster properties from an X-ray image deprojection analysis of 207 clusters of galaxies. Mon Not R Astron Soc. 1997;292:419–467.
-
- Peres CB, et al. A ROSAT study of the cores of clusters of galaxies—I. Cooling flows in an X-ray flux-limited sample. Mon Not R Astron Soc. 1998;298:416–432.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

