Luteinizing hormone stimulates mammalian target of rapamycin signaling in bovine luteal cells via pathways independent of AKT and mitogen-activated protein kinase: modulation of glycogen synthase kinase 3 and AMP-activated protein kinase
- PMID: 20351317
- PMCID: PMC2875818
- DOI: 10.1210/en.2009-1032
Luteinizing hormone stimulates mammalian target of rapamycin signaling in bovine luteal cells via pathways independent of AKT and mitogen-activated protein kinase: modulation of glycogen synthase kinase 3 and AMP-activated protein kinase
Abstract
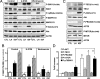
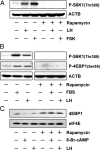
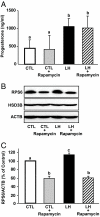
LH stimulates the production of cAMP in luteal cells, which leads to the production of progesterone, a hormone critical for the maintenance of pregnancy. The mammalian target of rapamycin (MTOR) signaling cascade has recently been examined in ovarian follicles where it regulates granulosa cell proliferation and differentiation. This study examined the actions of LH on the regulation and possible role of the MTOR signaling pathway in primary cultures of bovine corpus luteum cells. Herein, we demonstrate that activation of the LH receptor stimulates the phosphorylation of the MTOR substrates ribosomal protein S6 kinase 1 (S6K1) and eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E binding protein 1. The actions of LH were mimicked by forskolin and 8-bromo-cAMP. LH did not increase AKT or MAPK1/3 phosphorylation. Studies with pathway-specific inhibitors demonstrated that the MAPK kinase 1 (MAP2K1)/MAPK or phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/AKT signaling pathways were not required for LH-stimulated MTOR/S6K1 activity. However, LH decreased the activity of glycogen synthase kinase 3Beta (GSK3B) and AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK). The actions of LH on MTOR/S6K1 were mimicked by agents that modulated GSK3B and AMPK activity. The ability of LH to stimulate progesterone secretion was not prevented by rapamycin, a MTOR inhibitor. In contrast, activation of AMPK inhibited LH-stimulated MTOR/S6K1 signaling and progesterone secretion. In summary, the LH receptor stimulates a unique series of intracellular signals to activate MTOR/S6K1 signaling. Furthermore, LH-directed changes in AMPK and GSK3B phosphorylation appear to exert a greater impact on progesterone synthesis in the corpus luteum than rapamycin-sensitive MTOR-mediated events.
Figures





References
-
- Berisha B, Schams D 2005 Ovarian function in ruminants. Domest Anim Endocrinol 29:305–317 - PubMed
-
- Davis JS, Rueda BR 2002 The corpus luteum: an ovarian structure with maternal instincts and suicidal tendencies. Front Biosci 7:d1949–d1978 - PubMed
-
- Stocco C, Telleria C, Gibori G 2007 The molecular control of corpus luteum formation, function, and regression. Endocr Rev 28:117–149 - PubMed
-
- Marsh JM 1976 The role of cyclic AMP in gonadal steroidogenesis. Biol Reprod 14:30–53 - PubMed
-
- Niswender GD 2002 Molecular control of luteal secretion of progesterone. Reproduction 123:333–339 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

