Low-dose lipopolysaccharide selectively sensitizes hypoxic ischemia-induced white matter injury in the immature brain
- PMID: 20351655
- PMCID: PMC3608684
- DOI: 10.1203/PDR.0b013e3181df5f6b
Low-dose lipopolysaccharide selectively sensitizes hypoxic ischemia-induced white matter injury in the immature brain
Abstract
Little is known about roles of inflammation and hypoxic ischemia (HI) in the generation of neuroinflammation and damage of blood-brain barrier (BBB) in the white matter (WM) that displays regional vulnerability in preterm infants. We investigated whether low-dose lipopolysaccharide (LPS) sensitizes HI-induced WM injury in postpartum (P) day 2 rat pups by selectively increasing neuroinflammation and BBB damage in the WM. Pups received LPS (0.05 mg/kg) (LPS + HI) or normal saline (NS + HI) followed by 90-min HI. LPS and NS group were the pups that had LPS or NS only. Myelin basic protein immunohistochemistry on P11 showed WM injury in LPS + HI group, but not in NS + HI, LPS, and NS groups. In contrast, no gray matter injury was found in the four groups. LPS + HI group also showed decreased number of oligodendrocytes in the WM 72-h postinsult. In the same brain region, increases of activated microglia, TNF-alpha expression, BBB leakage, and cleaved caspase-3 positive cells were much more prominent in LPS + HI group than in the other three groups 24-h postinsult. The oligodendrocytes were the major cells with cleaved caspase-3 expression. We concluded that low-dose LPS sensitized HI-induced WM injury in the immature brain by selectively up-regulating neuroinflammation and BBB damage in the WM.
Figures
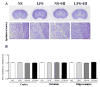
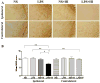

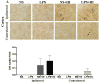

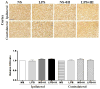






References
-
- Volpe JJ. Neurology of the Newborn. 5. W.B. Saunders Co; Philadelphia: 2008. pp. 370–379.pp. 433–436.
-
- Vincer MJ, Allen AC, Joseph KS, Stinson DA, Scot H, Wood E. Increasing prevalence of cerebral palsy among very preterm infants: a population-based study. Pediatrics. 2006;118:e1621–e1626. - PubMed
-
- Tsuji M, Saul JP, Plessis A, Eichenwald E, Sobh J, Crocker R, Volpe JJ. Cerebral intravascular oxygenation correlates with mean arterial pressure in critically ill premature infants. Pediatrics. 2000;106:625–632. - PubMed
-
- Stoll BJ, Hansen NI, Adams-Chapman I, Fanaroff AA, Hintz SR, Vohr B, Higgins RD for the National Institute of Child Health and Human development Neonatal Research Network. Neurodevelopmental and growth impairment among extremely low-birth-weight infants with neonatal infection. JAMA. 2004;292:2357–2365. - PubMed
-
- Yanowitz TD, Jordan JA, Gilmour CH, Towbin R, Bowen A, Roberts JM, Brozanski BS. Hemodynamic disturbances in premature infants born after chorioamnionitis: association with cord blood cytokine concentrations. Pediatr Res. 2002;51:310–316. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

