The AIM2 inflammasome is essential for host defense against cytosolic bacteria and DNA viruses
- PMID: 20351692
- PMCID: PMC2887480
- DOI: 10.1038/ni.1864
The AIM2 inflammasome is essential for host defense against cytosolic bacteria and DNA viruses
Abstract
Inflammasomes regulate the activity of caspase-1 and the maturation of interleukin 1beta (IL-1beta) and IL-18. AIM2 has been shown to bind DNA and engage the caspase-1-activating adaptor protein ASC to form a caspase-1-activating inflammasome. Using Aim2-deficient mice, we identify a central role for AIM2 in regulating caspase-1-dependent maturation of IL-1beta and IL-18, as well as pyroptosis, in response to synthetic double-stranded DNA. AIM2 was essential for inflammasome activation in response to Francisella tularensis, vaccinia virus and mouse cytomegalovirus and had a partial role in the sensing of Listeria monocytogenes. Moreover, production of IL-18 and natural killer cell-dependent production of interferon-gamma, events critical in the early control of virus replication, were dependent on AIM2 during mouse cytomegalovirus infection in vivo. Collectively, our observations demonstrate the importance of AIM2 in the sensing of both bacterial and viral pathogens and in triggering innate immunity.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

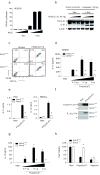

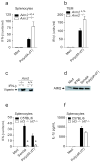

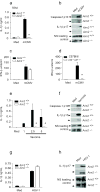
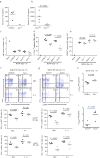
Comment in
-
AIMing 2 defend against intracellular pathogens.Nat Immunol. 2010 May;11(5):367-9. doi: 10.1038/ni0510-367. Nat Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20404848 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
The AIM2 inflammasome is critical for innate immunity to Francisella tularensis.Nat Immunol. 2010 May;11(5):385-93. doi: 10.1038/ni.1859. Epub 2010 Mar 28. Nat Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20351693 Free PMC article.
-
AIM2/ASC triggers caspase-8-dependent apoptosis in Francisella-infected caspase-1-deficient macrophages.Cell Death Differ. 2012 Oct;19(10):1709-21. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2012.51. Epub 2012 May 4. Cell Death Differ. 2012. PMID: 22555457 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of the AIM2, NLRC4, and NLRP3 inflammasomes in caspase-1 activation by Listeria monocytogenes.J Clin Immunol. 2010 Sep;30(5):693-702. doi: 10.1007/s10875-010-9425-2. Epub 2010 May 20. J Clin Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20490635 Free PMC article.
-
Francisella tularensis: activation of the inflammasome.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2007 Jun;1105:219-37. doi: 10.1196/annals.1409.005. Epub 2007 Mar 29. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2007. PMID: 17395724 Review.
-
Sensing cytoplasmic danger signals by the inflammasome.J Clin Immunol. 2010 Jul;30(4):512-9. doi: 10.1007/s10875-010-9419-0. Epub 2010 Apr 17. J Clin Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20401524 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Biting the hand that feeds: Metabolic determinants of cell fate during infection.Front Immunol. 2022 Oct 13;13:923024. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.923024. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36311735 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Critical Role for the DNA Sensor AIM2 in Stem Cell Proliferation and Cancer.Cell. 2015 Jul 2;162(1):45-58. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2015.06.001. Epub 2015 Jun 18. Cell. 2015. PMID: 26095253 Free PMC article.
-
NLR and Intestinal Dysbiosis-Associated Inflammatory Illness: Drivers or Dampers?Front Immunol. 2020 Aug 11;11:1810. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01810. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32903730 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inflammasome adaptor protein Apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing CARD (ASC) is critical for the immune response and survival in west Nile virus encephalitis.J Virol. 2013 Apr;87(7):3655-67. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02667-12. Epub 2013 Jan 9. J Virol. 2013. PMID: 23302887 Free PMC article.
-
[Caspase-1 regulates autoinflammation in rheumatic diseases].Z Rheumatol. 2016 Apr;75(3):265-75. doi: 10.1007/s00393-016-0077-3. Z Rheumatol. 2016. PMID: 27034076 Review. German.
References
-
- Kawai T, Akira S. Toll-like receptor and RIG-I-like receptor signaling. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2008;1143:1–20. - PubMed
-
- Takeda K, Akira S. Toll-like receptors in innate immunity. Int Immunol. 2005;17:1–14. - PubMed
-
- Yoneyama M, Fujita T. RIG-I family RNA helicases: cytoplasmic sensor for antiviral innate immunity. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2007;18:545–551. - PubMed
-
- Martinon F, Mayor A, Tschopp J. The inflammasomes: guardians of the body. Annu Rev Immunol. 2009;27:229–265. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

