Genetic variation in cholinergic muscarinic-2 receptor gene modulates M2 receptor binding in vivo and accounts for reduced binding in bipolar disorder
- PMID: 20351719
- PMCID: PMC2895691
- DOI: 10.1038/mp.2010.24
Genetic variation in cholinergic muscarinic-2 receptor gene modulates M2 receptor binding in vivo and accounts for reduced binding in bipolar disorder
Abstract
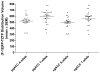
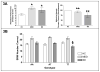
Genetic variation in the cholinergic muscarinic-2 (M(2)) receptor gene (CHRM2) has been associated with the risk for developing depression. We previously reported that M(2)-receptor distribution volume (V(T)) was reduced in depressed subjects with bipolar disorder (BD) relative to depressed subjects with major depressive disorder (MDD) and healthy controls (HCs). In this study, we investigated the effects of six single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) for CHRM2 on M(2)-receptor binding to test the hypotheses that genetic variation in CHRM2 influences M(2)-receptor binding and that a CHRM2 polymorphism underlies the deficits in M(2)-receptor V(T) observed in BD. The M(2)-receptor V(T) was measured using positron emission tomography and [(18)F]FP-TZTP in unmedicated, depressed subjects with BD (n=16) or MDD (n=24) and HCs (n=25), and the effect of genotype on V(T) was assessed. In the controls, one SNP (with identifier rs324650, in which the ancestral allele adenine (A) is replaced with one or two copies of thymine (T), showed a significant allelic effect on V(T) in the pregenual and subgenual anterior cingulate cortices in the direction AA<AT<TT. In contrast, in BD subjects with the TT genotype, V(T) was significantly lower than in BD subjects with the AT genotype in these regions. The BD subjects homozygous for the T -allele also showed markedly lower V(T) (by 27 to 37% across regions) than HCs of the same genotype. Post hoc analyses suggested that T homozygosity was associated with a more severe illness course, as manifested by lower socioeconomic function, poorer spatial recognition memory and a greater likelihood of having attempted suicide. These data represent novel preliminary evidence that reduced M(2)-receptor V(T) in BD is associated with genetic variation within CHRM2. The differential impact of the M(2)-receptor polymorphism at rs324650 in the BD and HC samples suggests interactive effects with an unidentified vulnerability factor for BD.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Positron emission tomography quantification of serotonin-1A receptor binding in medication-free bipolar depression.Biol Psychiatry. 2009 Aug 1;66(3):223-30. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2009.01.028. Epub 2009 Mar 17. Biol Psychiatry. 2009. PMID: 19278673 Free PMC article.
-
Reduced muscarinic type 2 receptor binding in subjects with bipolar disorder.Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2006 Jul;63(7):741-7. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.63.7.741. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2006. PMID: 16818863
-
Exploring the functional role of the CHRM2 gene in human cognition: results from a dense genotyping and brain expression study.BMC Med Genet. 2007 Nov 8;8:66. doi: 10.1186/1471-2350-8-66. BMC Med Genet. 2007. PMID: 17996044 Free PMC article.
-
Cognitive deficits in bipolar disorders: Implications for emotion.Clin Psychol Rev. 2018 Feb;59:126-136. doi: 10.1016/j.cpr.2017.11.006. Epub 2017 Nov 21. Clin Psychol Rev. 2018. PMID: 29195773 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The impact of COMT polymorphisms on cognition in Bipolar Disorder: A review: Special Section on "Translational and Neuroscience Studies in Affective Disorders" Section Editor, Maria Nobile MD, PhD. This Section of JAD focuses on the relevance of translational and neuroscience studies in providing a better understanding of the neural basis of affective disorders. The main aim is to briefly summaries relevant research findings in clinical neuroscience with particular regards to specific innovative topics in mood and anxiety disorders.J Affect Disord. 2019 Jan 15;243:545-551. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2018.08.009. Epub 2018 Aug 8. J Affect Disord. 2019. PMID: 30146088 Review.
Cited by
-
Neuronal-specific methylome and hydroxymethylome analysis reveal replicated and novel loci associated with alcohol use disorder.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Nov 29:2023.11.28.23299094. doi: 10.1101/2023.11.28.23299094. medRxiv. 2023. Update in: Front Genet. 2024 Apr 03;15:1345410. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2024.1345410. PMID: 38105948 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Muscarinic receptors: their roles in disorders of the central nervous system and potential as therapeutic targets.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2012 May;18(5):369-79. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-5949.2011.00249.x. Epub 2011 Feb 26. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2012. PMID: 22070219 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploration of Potential Ewing Sarcoma Drugs from FDA-Approved Pharmaceuticals through Computational Drug Repositioning, Pharmacogenomics, Molecular Docking, and MD Simulation Studies.ACS Omega. 2022 Jun 1;7(23):19243-19260. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.2c00518. eCollection 2022 Jun 14. ACS Omega. 2022. PMID: 35721972 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor Subtypes in the Mouse Amygdala Regulate Affective Behaviors and Response to Social Stress.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2016 May;41(6):1579-87. doi: 10.1038/npp.2015.316. Epub 2015 Oct 16. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2016. PMID: 26471256 Free PMC article.
-
The anterior cingulate cortex may enhance inhibition of lateral prefrontal cortex via m2 cholinergic receptors at dual synaptic sites.J Neurosci. 2012 Oct 31;32(44):15611-25. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2339-12.2012. J Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 23115196 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cannon DM, Carson RE, Nugent AC, Eckelman WC, Kiesewetter DO, Williams J, et al. Reduced muscarinic type 2 receptor binding in subjects with bipolar disorder. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2006 Jul;63(7):741–747. - PubMed
-
- Jagoda EM, Kiesewetter DO, Shimoji K, Ravasi L, Yamada M, Gomeza J, et al. Regional brain uptake of the muscarinic ligand, [18F]FP-TZTP, is greatly decreased in M2 receptor knockout mice but not in M1, M3 and M4 receptor knockout mice. Neuropharmacology. 2003 Apr;44(5):653–661. - PubMed
-
- Carson RE, Kiesewetter DO, Jagoda E, Der MG, Herscovitch P, Eckelman WC. Muscarinic cholinergic receptor measurements with [18F]FP-TZTP: control and competition studies. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1998 Oct;18(10):1130–1142. - PubMed
-
- Wang JC, Hinrichs AL, Stock H, Budde J, Allen R, Bertelsen S, et al. Evidence of common and specific genetic effects: association of the muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 (CHRM2) gene with alcohol dependence and major depressive syndrome. Hum Mol Genet. 2004 Sep 1;13(17):1903–1911. - PubMed
-
- Comings DE, Wu S, Rostamkhani M, McGue M, Iacono WG, MacMurray JP. Association of the muscarinic cholinergic 2 receptor (CHRM2) gene with major depression in women. Am J Med Genet. 2002 Jul 8;114(5):527–529. - PubMed

