Ribbing disease
- PMID: 20351994
- PMCID: PMC2844749
- DOI: 10.4103/0971-3026.59754
Ribbing disease
Abstract
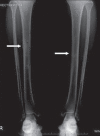
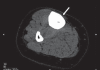
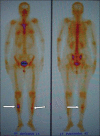
Ribbing disease is a rare sclerosing dysplasia that involves long tubular bones, especially the tibia and femur. It occurs after puberty and is reported to be more common in women. In this article we describe how Ribbing disease can be differentiated from diseases like Engelmann-Camurati disease, van Buchem disease, Erdheim-Chester disease, osteoid osteoma, chronic osteomyelitis, stress fracture, etc.
Keywords: Ribbing disease; imaging; sclerosing.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Seeger LL, Hewel KC, Yao L, Gold RH, Mirra JM, Chandnani VP, et al. Ribbing disease: Imaging and differential diagnosis. AJR A J Roentegol. 1996;167:689–94. - PubMed
-
- Abdul-Karim FW, Carter JR, Makley JT, Morrison SC, Helper SD, Joyce MJ, et al. Intramedullary osteosclerosis: Report of the clinicopathologic features of five cases. Orthopedics. 1988;11:1667–75. - PubMed
-
- Chanchairujira K, Chung CB, Lai YM, Haghighi P, Resnick D. Intramedullary Osteosclerosis: Imaging Features in Nine Patients. Radiology. 2001;220:25–230. - PubMed
-
- Ribbing S. Hereditary multiple diaphyseal sclerosis. Acta Radiol. 1949;31:522–36. - PubMed
-
- Ziran N, Hill S, Wright ME, Kovacs J, Robey PG, Wientroub S, et al. Ribbing Disease: Radiographic and biochemical characterization, lack of response to pamidronate. Skeletal Radiol. 2002;31:714–9. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

