Effect of bacterial inoculation, plant genotype and developmental stage on root-associated and endophytic bacterial communities in potato (Solanum tuberosum)
- PMID: 20352404
- PMCID: PMC2847171
- DOI: 10.1007/s10482-010-9421-9
Effect of bacterial inoculation, plant genotype and developmental stage on root-associated and endophytic bacterial communities in potato (Solanum tuberosum)
Abstract
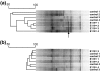
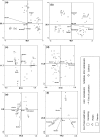
Beneficial bacteria interact with plants by colonizing the rhizosphere and roots followed by further spread through the inner tissues, resulting in endophytic colonization. The major factors contributing to these interactions are not always well understood for most bacterial and plant species. It is believed that specific bacterial functions are required for plant colonization, but also from the plant side specific features are needed, such as plant genotype (cultivar) and developmental stage. Via multivariate analysis we present a quantification of the roles of these components on the composition of root-associated and endophytic bacterial communities in potato plants, by weighing the effects of bacterial inoculation, plant genotype and developmental stage. Spontaneous rifampicin resistant mutants of two bacterial endophytes, Paenibacillus sp. strain E119 and Methylobacterium mesophilicum strain SR1.6/6, were introduced into potato plants of three different cultivars (Eersteling, Robijn and Karnico). Densities of both strains in, or attached to potato plants were measured by selective plating, while the effects of bacterial inoculation, plant genotype and developmental stage on the composition of bacterial, Alphaproteobacterial and Paenibacillus species were determined by PCR-denaturing gradient gel-electrophoresis (DGGE). Multivariate analyses revealed that the composition of bacterial communities was mainly driven by cultivar type and plant developmental stage, while Alphaproteobacterial and Paenibacillus communities were mainly influenced by bacterial inoculation. These results are important for better understanding the effects of bacterial inoculations to plants and their possible effects on the indigenous bacterial communities in relation with other plant factors such as genotype and growth stage.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Endophytic colonization of potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) by a novel competent bacterial endophyte, Pseudomonas putida strain P9, and its effect on associated bacterial communities.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2009 Jun;75(11):3396-406. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00491-09. Epub 2009 Mar 27. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2009. PMID: 19329656 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of plant genotype and growth stage on the betaproteobacterial communities associated with different potato cultivars in two fields.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2010 Jun;76(11):3675-84. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00040-10. Epub 2010 Apr 2. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 20363788 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of plant genotype and growth stage on the structure of bacterial communities associated with potato (Solanum tuberosum L.).FEMS Microbiol Ecol. 2008 May;64(2):283-96. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6941.2008.00469.x. Epub 2008 Mar 18. FEMS Microbiol Ecol. 2008. PMID: 18355298
-
Mechanisms and recent advances in biological control mediated through the potato rhizosphere.FEMS Microbiol Ecol. 2011 Mar;75(3):351-64. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6941.2010.01023.x. Epub 2011 Jan 12. FEMS Microbiol Ecol. 2011. PMID: 21204870 Review.
-
Plant beneficial endophytic bacteria: Mechanisms, diversity, host range and genetic determinants.Microbiol Res. 2019 Apr;221:36-49. doi: 10.1016/j.micres.2019.02.001. Epub 2019 Feb 4. Microbiol Res. 2019. PMID: 30825940 Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of Plant Growth-Promoting Bacteria (PGPB) Inoculation on the Growth, Antioxidant Activity, Cu Uptake, and Bacterial Community Structure of Rape (Brassica napus L.) Grown in Cu-Contaminated Agricultural Soil.Front Microbiol. 2019 Jun 27;10:1455. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.01455. eCollection 2019. Front Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31316489 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of the Inoculant Strain Pseudomonas sp. SPN31 nah + and of 2-Methylnaphthalene Contamination on the Rhizosphere and Endosphere Bacterial Communities of Halimione portulacoides.Curr Microbiol. 2017 May;74(5):575-583. doi: 10.1007/s00284-017-1197-y. Epub 2017 Mar 4. Curr Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28260118
-
A New Approach to Modify Plant Microbiomes and Traits by Introducing Beneficial Bacteria at Flowering into Progeny Seeds.Front Microbiol. 2017 Jan 23;8:11. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.00011. eCollection 2017. Front Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28167932 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of soil bacterial communities in integrated crop production systems within the Amazon Biome, Brazil: a comparative study.Braz J Microbiol. 2024 Sep;55(3):2815-2825. doi: 10.1007/s42770-024-01352-8. Epub 2024 May 2. Braz J Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38696039 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of plant-bacteria interactions in their native habitat: bacterial communities associated with wild tobacco are independent of endogenous jasmonic acid levels and developmental stages.PLoS One. 2014 Apr 11;9(4):e94710. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0094710. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24728407 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Andreote FD, Gullo MJM, Lima AOS, Maccheroni W, Jr, Azevedo JL, Araujo WL. Impact of genetically modified Enterobacter cloacae on indigenous endophytic community of Citrus sinensis seedlings. J Microbiol. 2004;42:169–173. - PubMed
-
- Andreote FD, Mendes R, Dini-Andreote F, Rossetto PB, Labate CA, Pizzirani-Kleiner CA, van Elsas JD, Azevedo JL, Araújo WL. Transgenic tobacco revealing altered bacterial diversity in the rhizosphere during early plant development. Antonie Leeuwenhoek. 2008;93:415–424. doi: 10.1007/s10482-007-9219-6. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Andreote FD, Rossetto PB, Mendes R, Avila LA, Labate CA, Pizzirani-Kleiner AA, Azevedo JL, Araújo WL. Bacterial community in the rhizosphere and rhizoplane of wild type and transgenic eucalyptus. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2009;25:1065–1073. doi: 10.1007/s11274-009-9990-9. - DOI
-
- Andreote FD, Carneiro RT, Salles JF, Marcon J, Labate CA, Azevedo JL, Araújo WL. Culture-independent assessment of Alphaproteobacteria related to order Rhizobiales and the diversity of cultivated Methylobacterium in the rhizosphere and rhizoplane of transgenic eucalyptus. Microbial Ecol. 2009;57:82–93. doi: 10.1007/s00248-008-9405-8. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

