In vivo evaluation of (64)Cu-labeled magnetic nanoparticles as a dual-modality PET/MR imaging agent
- PMID: 20353170
- PMCID: PMC2865436
- DOI: 10.1021/bc900511j
In vivo evaluation of (64)Cu-labeled magnetic nanoparticles as a dual-modality PET/MR imaging agent
Abstract
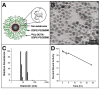
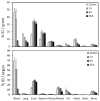
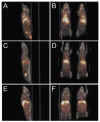
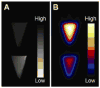
A novel nanoparticle-based dual-modality positron emission tomograph/magnetic resonance imaging (PET/MRI) contrast agent was developed. The probe consisted of a superparamagnetic iron oxide (SPIO) core coated with PEGylated phospholipids. The chelator 1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclo-dodecane-1,4,7,10-tetraacetic acid (DOTA) was conjugated to PEG termini to allow labeling with positron-emitting (64)Cu. Radiolabeling with (64)Cu at high yield and high purity was readily achieved. The (64)Cu-SPIO probes produced strong MR and PET signals and were stable in mouse serum for 24 h at 37 degrees C. Biodistribution and in vivo PET/CT imaging studies of the probes showed a circulation half-life of 143 min and high initial blood retention with moderate liver uptake, making them an attractive contrast agent for disease studies.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The cell labeling efficacy, cytotoxicity and relaxivity of copper-activated MRI/PET imaging contrast agents.Biomaterials. 2011 Feb;32(4):1167-76. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2010.10.013. Epub 2010 Oct 28. Biomaterials. 2011. PMID: 21035183
-
Synthesis of 64Cu-labeled magnetic nanoparticles for multimodal imaging.Bioconjug Chem. 2008 Jul;19(7):1496-504. doi: 10.1021/bc800108v. Epub 2008 Jun 26. Bioconjug Chem. 2008. PMID: 18578485 Free PMC article.
-
Site-specific conjugation of monodispersed DOTA-PEGn to a thiolated diabody reveals the effect of increasing peg size on kidney clearance and tumor uptake with improved 64-copper PET imaging.Bioconjug Chem. 2011 Apr 20;22(4):709-16. doi: 10.1021/bc100464e. Epub 2011 Mar 24. Bioconjug Chem. 2011. PMID: 21395337 Free PMC article.
-
PET Imaging of HER2-Positive Tumors with Cu-64-Labeled Affibody Molecules.Mol Imaging Biol. 2019 Oct;21(5):907-916. doi: 10.1007/s11307-018-01310-5. Mol Imaging Biol. 2019. PMID: 30617730
-
Polyethylene glycol–coated and folic acid–conjugated superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles.2009 Sep 30 [updated 2009 Nov 12]. In: Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2004–2013. 2009 Sep 30 [updated 2009 Nov 12]. In: Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2004–2013. PMID: 20641868 Free Books & Documents. Review.
Cited by
-
High-throughput quantitative microscopy-based half-life measurements of intravenously injected agents.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Feb 18;117(7):3502-3508. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1915450117. Epub 2020 Feb 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 32015123 Free PMC article.
-
Nanogel star polymer architectures: a nanoparticle platform for modular programmable macromolecular self-assembly, intercellular transport, and dual-mode cargo delivery.Adv Mater. 2011 Oct 18;23(39):4509-15. doi: 10.1002/adma.201102371. Epub 2011 Sep 8. Adv Mater. 2011. PMID: 21901765 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Tumor lysing genetically engineered T cells loaded with multi-modal imaging agents.Sci Rep. 2014 Mar 28;4:4502. doi: 10.1038/srep04502. Sci Rep. 2014. PMID: 24675806 Free PMC article.
-
Radiolabeled theranostics: magnetic and gold nanoparticles.Bioimpacts. 2016;6(3):169-181. doi: 10.15171/bi.2016.23. Epub 2016 Sep 30. Bioimpacts. 2016. PMID: 27853680 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The use of molecular imaging combined with genomic techniques to understand the heterogeneity in cancer metastasis.Br J Radiol. 2014 Jun;87(1038):20140065. doi: 10.1259/bjr.20140065. Epub 2014 Mar 6. Br J Radiol. 2014. PMID: 24597512 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Czernin J, Allen-Auerbach M, Schelbert H. Improvements in Cancer Staging with PET/CT: Literature-Based Evidence as of September 2006. Journal of Nuclear Medicine. 2007;48:78S. - PubMed
-
- Judenhofer MS, Wehrl HF, Newport DF, Catana C, Siegel SB, Becker M, Thielscher A, Kneilling M, Lichy MP, Eichner M, Klingel K, Reischl G, Widmaier S, Rocken M, Nutt RE, Machulla HJ, Uludag K, Cherry SR, Claussen CD, Pichler BJ. Simultaneous PET-MRI: a new approach for functional and morphological imaging. Nat Med. 2008;14:459–465. - PubMed
-
- Higuchi T, Anton M, Dumler K, Seidl S, Pelisek J, Saraste A, Welling A, Hofmann F, Oostendorp RA, Gansbacher B, Nekolla SG, Bengel FM, Botnar RM, Schwaiger M. Combined reporter gene PET and iron oxide MRI for monitoring survival and localization of transplanted cells in the rat heart. J Nucl Med. 2009;50:1088–1094. - PubMed
-
- Xu H, Regino CA, Koyama Y, Hama Y, Gunn AJ, Bernardo M, Kobayashi H, Choyke PL, Brechbiel MW. Preparation and preliminary evaluation of a biotin-targeted, lectin-targeted dendrimer-based probe for dual-modality magnetic resonance and fluorescence imaging. Bioconjug Chem. 2007;18:1474–1482. - PubMed
-
- Koyama Y, Talanov VS, Bernardo M, Hama Y, Regino CA, Brechbiel MW, Choyke PL, Kobayashi H. A dendrimer-based nanosized contrast agent dual-labeled for magnetic resonance and optical fluorescence imaging to localize the sentinel lymph node in mice. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2007;25:866–871. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

