A quantitative trait locus responsible for inducing B-cell lymphoblastic lymphoma is a hotspot for microsatellite instability
- PMID: 20353532
- PMCID: PMC11159001
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2009.01437.x
A quantitative trait locus responsible for inducing B-cell lymphoblastic lymphoma is a hotspot for microsatellite instability
Abstract
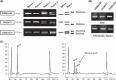
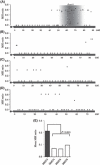
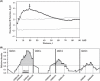
While the molecular mechanisms underlying microsatellite instability (MSI) have been exhaustively investigated, identifying the patterns of MSI distribution within diverse cancer genomes has remained an elusive issue. In the present study, we conducted genome-wide MSI screening in B-cell lymphoblastic lymphomas (B-LBL) which spontaneously develop in the SL/Kh strain of mice. Tumor samples harvested from 16 mice were investigated using a framework map consisting of 150 microsatellite markers spaced at increments of roughly 0.5-3.0 centimorgans, spanning the entirety of mouse chromosomes (mus musculus chromosomes [MMU]) 3-6. MMU3 contains a quantitative trait locus (QTL), Bomb1 (bone marrow pre-B1), known to induce an aberrant expansion of pre-B cells in bone marrow prior to the onset of B-LBL in SL/Kh mice. The remaining chromosomes were selected on the basis of those most closely resembling MMU3 in terms of total estimated length (maximum variance 10 Mb). MSI was confirmed at 2<or= markers in DNA derived from tumor tissues in 15 SL/Kh mice (93.7%), while healthy splenic DNA samples screened in parallel were consistently negative for MSI. The overall MSI incidence was significantly higher on MMU3 compared with MMU4-6 (P = 0.031). Additionally, by applying spatial point pattern analysis combined with a 1-D version of Ripley's K-function, we successfully demonstrated the predilection of MSI-susceptible loci to structure a massive cluster within the Bomb1 locus. Our study is the first to suggest that a QTL concomitantly serves as a hotspot for MSI-susceptible loci and sheds new light on somatic cancer genetics.
Figures
References
-
- Soslow RA, Baergen RN, Warnke RA. B‐Lineage lymphoblastic lymphoma is a clinicopathologic entity distinct from other histologically similar aggressive lymphomas with blastic morphology. Cancer 1999; 85: 2648–54. - PubMed
-
- Cheng A‐L, Su I‐J, Tien H‐F, Wang C‐C, Chen Y‐C, Wang C‐H. Characteristic clinicopathologic features of adult B‐cell lymphoblastic lymphoma with special emphasis on differential diagnosis with an atypical form probably of blastic lymphocytic lymphoma of intermediate differentiation origin. Cancer 1994; 73: 706–10. - PubMed
-
- Sander CA, Jaffe ES, Gebhardt FC, Yano T, Medeiros LJ. Mediastinal lymphoblastic lymphoma with an immature B‐cell immunophenotype. Am J Surg Pathol 1992; 16: 300–5. - PubMed
-
- Link MP, Roper M, Dorfman RF, Crist WM, Cooper MD, Levy R. Cutaneous lymphoblastic lymphoma with pre‐B markers. Blood 1983; 61: 838–41. - PubMed
-
- Pattengale PK, Frith CH. Immunomorphologic classification of spontaneous lymphoid cell neoplasms occurring in female BALB/c mice. J Natl Cancer Inst 1983; 70: 169–79. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

