Elevated endotoxin levels in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
- PMID: 20353583
- PMCID: PMC2873499
- DOI: 10.1186/1476-9255-7-15
Elevated endotoxin levels in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
Abstract
Background: Emerging data indicate that gut-derived endotoxin may contribute to low-grade systemic inflammation in insulin resistant states. This study aimed to examine the importance of serum endotoxin and inflammatory markers in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) patients, with and without type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), and to explore the effect of treatment with a lipase inhibitor, Orlistat, on their inflammatory status.
Methods: Fasted serum from 155 patients with biopsy proven NAFLD and 23 control subjects were analysed for endotoxin, soluble CD14 (sCD14), soluble tumour necrosis factor receptor II (sTNFRII) and various metabolic parameters. A subgroup of NAFLD patients were re-assessed 6 and 12 months after treatment with diet alone (n = 6) or diet plus Orlistat (n = 8).
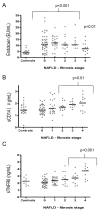
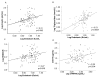
Results: Endotoxin levels were significantly higher in patients with NAFLD compared with controls (NAFLD: 10.6(7.8, 14.8) EU/mL; controls: 3.9(3.2, 5.2) EU/mL, p < 0.001); NAFLD alone produced comparable endotoxin levels to T2DM (NAFLD: T2DM: 10.6(5.6, 14.2) EU/mL; non-diabetic: 10.6(8.5, 15.2) EU/mL), whilst a significant correlation between insulin resistance and serum endotoxin was observed (r = 0.27, p = 0.008). Both sCD14 (p < 0.01) and sTNFRII (p < 0.001) increased with severity of fibrosis. A positive correlation was also noted between sTNFRII and sCD14 in the NAFLD subjects (r = 0.29, p = 0.004).Sub-cohort treatment with Orlistat in patients with NAFLD showed significant decreases in ALT (p = 0.006), weight (p = 0.005) and endotoxin (p = 0.004) compared with the NAFLD, non-Orlistat treated control cohort at 6 and 12 months post therapy, respectively.
Conclusions: Endotoxin levels were considerably increased in NAFLD patients, with marked increases noted in early stage fibrosis compared with controls. These results suggest elevated endotoxin may serve as an early indicator of potential liver damage, perhaps negating the need for invasive liver biopsy. As endotoxin may promote insulin resistance and inflammation, interventions aimed at reducing endotoxin levels in NAFLD patients may prove beneficial in reducing inflammatory burden.
Figures
References
-
- Bellentani S, Saccoccio G, Masutti F, Crocè LS, Brandi G, Sasso F, Cristanini G, Tiribelli C. Prevalence of and risk factors for hepatic steatosis in Northern Italy. Ann Intern Med. 2000;132(2):112–117. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

