No effect of epoprostenol on right ventricular diameter in patients with acute pulmonary embolism: a randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 20353588
- PMCID: PMC2859373
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2466-10-18
No effect of epoprostenol on right ventricular diameter in patients with acute pulmonary embolism: a randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Background: Right ventricular dilatation in the setting of acute pulmonary embolism is associated with an adverse prognosis. Treatment with a pulmonary vasodilator has never been studied systematically. We evaluated the effect of epoprostenol on right ventricular diameter and function in patients with acute pulmonary embolism and right ventricular dilatation.
Methods: In a randomized, single-blind study, 14 patients with acute pulmonary embolism received epoprostenol or placebo infusion for 24 hours on top of conventional treatment. Effects on right ventricular end-diastolic diameter, systolic pulmonary artery pressure, right ventricle fractional area change and tricuspid annular plane systolic excursion were assessed by serial echocardiography. Furthermore Troponin T and NT-proBNP were measured serially.
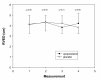
Results: Compared to placebo, epoprostenol was associated with a relative change from baseline in right ventricular end-diastolic diameter of +2% after 2.5 hours and -8% after 24 hours. Epoprostenol did not have a significant effect on systolic pulmonary artery pressure, right ventricular fractional area change and tricuspid annular plane systolic excursion, nor on biochemical parameters.
Conclusion: In patients with acute pulmonary embolism and right ventricular overload, treatment with epoprostenol did not improve right ventricular dilatation or any other measured variables of right ventricular overload.
Registration: URL: NCT01014156Medical ethical committee: Medisch-ethische toetsingscommissie (METc) from the VUmc (free university medical centre).
Figures


Similar articles
-
Regional right ventricular dysfunction in acute pulmonary embolism: relationship with clot burden and biomarker profile.Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2016 Mar;32(3):389-98. doi: 10.1007/s10554-015-0780-1. Epub 2015 Oct 1. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2016. PMID: 26428674
-
Assessing the severity of pulmonary embolism among patients in the emergency department: Utility of RV/LV diameter ratio.PLoS One. 2020 Nov 19;15(11):e0242340. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0242340. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 33211719 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of right ventricular dysfunction and end-diastolic pulmonary artery pressure estimated from analysis of tricuspid regurgitant velocity spectrum in patients with preserved ejection fraction.Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2019 Apr 1;20(4):446-454. doi: 10.1093/ehjci/jey116. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2019. PMID: 30169769
-
What are the echocardiographic findings of acute right ventricular strain that suggest pulmonary embolism?Anaesth Crit Care Pain Med. 2021 Apr;40(2):100852. doi: 10.1016/j.accpm.2021.100852. Epub 2021 Mar 26. Anaesth Crit Care Pain Med. 2021. PMID: 33781986 Review.
-
Echocardiography in the Evaluation of Pulmonary Embolism.Cardiol Rev. 2017 Nov/Dec;25(6):309-314. doi: 10.1097/CRD.0000000000000158. Cardiol Rev. 2017. PMID: 28767504 Review.
Cited by
-
Hemodynamic and respiratory support in pulmonary embolism: a narrative review.Front Med (Lausanne). 2023 Jun 2;10:1123793. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1123793. eCollection 2023. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37332759 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Changes in Pulmonary Vascular Resistance and Obstruction Score Following Acute Pulmonary Embolism in Pigs.Crit Care Explor. 2024 Feb 2;6(2):e1040. doi: 10.1097/CCE.0000000000001040. eCollection 2024 Feb. Crit Care Explor. 2024. PMID: 38511125 Free PMC article.
-
Supplemental oxygen for pulmonary embolism (SO-PE): study protocol for a mechanistic, randomised, blinded, cross-over study.BMJ Open. 2024 Nov 12;14(11):e091567. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2024-091567. BMJ Open. 2024. PMID: 39532350 Free PMC article.
-
Gas exchange and pulmonary hypertension following acute pulmonary thromboembolism: has the emperor got some new clothes yet?Pulm Circ. 2014 Jun;4(2):220-36. doi: 10.1086/675985. Pulm Circ. 2014. PMID: 25006441 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immediate cardiopulmonary responses to consecutive pulmonary embolism: a randomized, controlled, experimental study.BMC Pulm Med. 2024 May 14;24(1):233. doi: 10.1186/s12890-024-03006-9. BMC Pulm Med. 2024. PMID: 38745282 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Frémont B, Pacouret G, Jacobi D, Puglisi R, Charbonnier B, de Labriolle A. Prognostic value of echocardiographic right/left ventricular end-diastolic diameter ratio in patients with acute pulmonary embolism. Results from a monocenter registry of 1,416 patients. Chest. 2008;133:358–362. doi: 10.1378/chest.07-1231. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Grifoni S, Olivotto I, Cecchini P, Pieralli F, Camaii A, Santoro G, Conti A, Agnelli G, Berni G. Short-term clinical outcome of patients with acute pulmonary embolism, normal blood pressure, and echocardiographic right ventricular dysfunction. Circulation. 2000;101:2817–2822. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

