Protective effects of Spirulina maxima on hyperlipidemia and oxidative-stress induced by lead acetate in the liver and kidney
- PMID: 20353607
- PMCID: PMC2859351
- DOI: 10.1186/1476-511X-9-35
Protective effects of Spirulina maxima on hyperlipidemia and oxidative-stress induced by lead acetate in the liver and kidney
Abstract
Background: Oxidative damage has been proposed as a possible mechanism involved in lead toxicity, specially affecting the liver and kidney. Previous studies have shown the antioxidant effect of Spirulina maxima in several experimental models of oxidative stress. The current study was carried out to evaluate the antioxidant activity of Spirulina maxima against lead acetate-induced hyperlipidemia and oxidative damage in the liver and kidney of male rats. Control animals were fed on a standard diet and did not receive lead acetate (Control group). Experimental animals were fed on a standard laboratory diet with or without Spirulina maxima 5% in the standard laboratory diet and treated with three doses of lead acetate (25 mg each/weekly, intraperitoneal injection) (lead acetate with Spirulina, and lead acetate without Spirulina groups).
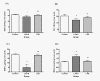
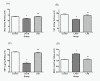
Results: The results showed that Spirulina maxima prevented the lead acetate-induced significant changes on plasma and liver lipid levels and on the antioxidant status of the liver and kidney. On the other hand, Spirulina maxima succeeded to improve the biochemical parameters of the liver and kidney towards the normal values of the Control group.
Conclusions: It was concluded that Spirulina maxima has protective effects on lead acetate-induced damage, and that the effects are associated with the antioxidant effect of Spirulina.
Figures
References
-
- Shotyk W, Le Roux G. Biogeochemistry and cycling of lead. Met Ions Biol Syst. 2005;43:239–275. - PubMed
-
- Ademuyiwa O, Ugbaja RN, Rotimi SO, Abam E, Okediran BS, Dosumu OA, Onunkwor BO. Erythrocyte acetylcholinesterase activity as a surrogate indicator of lead-induced neurotoxicity in occupational lead exposure in Abeokuta, Nigeria. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 2007;24:183–188. doi: 10.1016/j.etap.2007.05.002. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

