Differential expression of KCNQ1 K+ channel in tubular cells of frog kidney
- PMID: 20353914
- PMCID: PMC3167289
- DOI: 10.4081/ejh.2010.e7
Differential expression of KCNQ1 K+ channel in tubular cells of frog kidney
Abstract
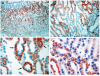
The aim of this study was to evaluate KCNQ1 K+ channel expression in the frog kidney of Rana esculenta. KCNQ1 K+ channel, also known as KvLQT1, is the pore forming a-subunit of the IKs K+ channel, a delayed rectifier voltage-gated K+ channel, which has an important role in water and salt transport in the kidney and gastrointestinal tract. The expression of KCNQ1 K+ channel along tubular epithelium differs from species to species. In the present study the expression of KCNQ1 K+ channel in the frog kidney has been demonstrated by immunohistochemistry. The presence of KCNQ1 K+ channel was demonstrated in the epithelial cells of distal convoluted tubule and collecting duct. However, the pattern of expression of KCNQ1 K+ channel differs between distal convoluted tubules and collecting duct. All epithelial cells of distal convoluted tubules revealed basolateral expression of KCNQ1 K+ channel. On the contrary, only the single cells of collecting duct, probably intercalated cells, showed diffuse cell surface staining with antibodies against KCNQ1 K+ channel. These findings suggest that KCNQ1 K+ channel has cell-specific roles in renal potassium ion transport.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cellular distribution of the potassium channel KCNQ1 in normal mouse kidney.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2007 Jan;292(1):F456-66. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00087.2006. Epub 2006 Aug 8. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2007. PMID: 16896189
-
Absence of KCNQ1-dependent K+ fluxes in proximal tubular cells of frog kidney.Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol. 2007 Nov;148(3):635-44. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2007.08.010. Epub 2007 Aug 15. Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17869561
-
KCNQ1-dependent transport in renal and gastrointestinal epithelia.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005 Dec 6;102(49):17864-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0505860102. Epub 2005 Nov 28. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005. PMID: 16314573 Free PMC article.
-
Renal potassium channels: recent developments.Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2004 Sep;13(5):549-55. doi: 10.1097/00041552-200409000-00011. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2004. PMID: 15300162 Review.
-
Collecting duct intercalated cell function and regulation.Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2015 Feb 6;10(2):305-24. doi: 10.2215/CJN.08880914. Epub 2015 Jan 28. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2015. PMID: 25632105 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Voltage-gated ion channels as novel regulators of epithelial ion transport in the osmoregulatory organs of insects.Front Insect Sci. 2024 May 21;4:1385895. doi: 10.3389/finsc.2024.1385895. eCollection 2024. Front Insect Sci. 2024. PMID: 38835480 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Histochemistry through the years, browsing a long-established journal: novelties in traditional subjects.Eur J Histochem. 2010 Dec 16;54(4):e51. doi: 10.4081/ejh.2010.e51. Eur J Histochem. 2010. PMID: 21263750 Free PMC article.
-
On the future contents of a small journal of histochemistry.Eur J Histochem. 2012 Dec 10;56(4):e51. doi: 10.4081/ejh.2012.e51. Eur J Histochem. 2012. PMID: 23361247 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of transport in the connecting tubule and cortical collecting duct.Compr Physiol. 2012 Apr;2(2):1541-84. doi: 10.1002/cphy.c110052. Compr Physiol. 2012. PMID: 23227301 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Basolateral membrane K+ channels in renal epithelial cells.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2012 May 1;302(9):F1069-81. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00646.2011. Epub 2012 Feb 15. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22338089 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bleich M, Shan Qi-X. Epithelial K+ channels: driving force generation and K+ recycling for epithelial transport with physiological and clinical implications. Acta Physiologica Sinica. 2007;59:443–53. - PubMed
-
- Jespersen T, Grunnet M, Olesen SP. The KCNQ1 potassium channel: from gene to physiological function. Physiology. 2005;20:408–16. - PubMed
-
- Lang F, Vallon V, Knipper M, Wangemann P. Functional significance of channels and transporters expressed in the inner ear and kidney. Am J Physiol. 2007;293:1187–208. - PubMed
-
- Robbins J. KCNQ potassium channels: physiology, pathophysiology, and pharmacology. Pharmacol Therapeutics. 2001;90:1–19. - PubMed
-
- Bleich M, Warth R. The very small-conductance K channel KvLQT1 and epithelial function. Pflugers Arch. 2000;440:202–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

