Activation of noncanonical NF-kappaB signaling by the oncoprotein Tio
- PMID: 20353939
- PMCID: PMC2878063
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.102848
Activation of noncanonical NF-kappaB signaling by the oncoprotein Tio
Abstract
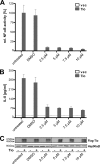
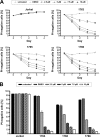
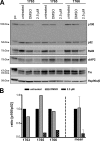
NF-kappaB transcription factors are key regulators of cellular proliferation and frequently contribute to oncogenesis. The herpesviral oncoprotein Tio, which promotes growth transformation of human T cells in a recombinant herpesvirus saimiri background, potently induces canonical NF-kappaB signaling through membrane recruitment of the ubiquitin ligase tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 6 (TRAF6). Here, we show that, in addition to Tio-TRAF6 interaction, the Tio-induced canonical NF-kappaB signal requires the presence of the regulatory subunit of the inhibitor of kappaB kinase (IKK) complex, NF-kappaB essential modulator (NEMO), and the activity of its key kinase, IKKbeta, to up-regulate expression of endogenous cellular inhibitor of apoptosis 2 (cIAP2) and interleukin 8 (IL-8) proteins. Dependent on TRAF6 and NEMO, Tio enhances the expression of the noncanonical NF-kappaB proteins, p100 and RelB. Independent of TRAF6 and NEMO, Tio mediates stabilization of the noncanonical kinase, NF-kappaB-inducing kinase (NIK). Concomitantly, Tio induces efficient processing of the p100 precursor molecule to its active form, p52, as well as DNA binding of nuclear p52 and RelB. In human T cells transformed by infection with a Tio-recombinant virus, sustained expression of p100, RelB, and cIAP2 depends on IKKbeta activity, yet processing to p52 remains largely unaffected by IKKbeta inhibition. However, long term inhibition of IKKbeta disrupts the continuous growth of the transformed cells and induces cell death. Hence, the Tio oncoprotein triggers noncanonical NF-kappaB signaling through NEMO-dependent up-regulation of p100 precursor and RelB, as well as through NEMO-independent generation of p52 effector.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Epstein-Barr virus latent infection membrane protein 1 TRAF-binding site induces NIK/IKK alpha-dependent noncanonical NF-kappaB activation.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004 Jan 6;101(1):141-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2237183100. Epub 2003 Dec 22. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004. PMID: 14691250 Free PMC article.
-
Maximal adamantyl-substituted retinoid-related molecule-induced apoptosis requires NF-κB noncanonical and canonical pathway activation.Cell Death Differ. 2011 Jan;18(1):164-73. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2010.84. Epub 2010 Jul 30. Cell Death Differ. 2011. PMID: 20671747 Free PMC article.
-
The NF-κB subunit RelB controls p100 processing by competing with the kinases NIK and IKK1 for binding to p100.Sci Signal. 2016 Sep 27;9(447):ra96. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.aad9413. Sci Signal. 2016. PMID: 27678221
-
The noncanonical NF-κB pathway.Immunol Rev. 2012 Mar;246(1):125-40. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2011.01088.x. Immunol Rev. 2012. PMID: 22435551 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Non-canonical NF-κB signaling pathway.Cell Res. 2011 Jan;21(1):71-85. doi: 10.1038/cr.2010.177. Epub 2010 Dec 21. Cell Res. 2011. PMID: 21173796 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
NF-κB and cancer: a paradigm of Yin-Yang.Am J Cancer Res. 2011;1(2):192-221. Epub 2010 Dec 6. Am J Cancer Res. 2011. PMID: 21969033 Free PMC article.
-
Actin-dependent activation of serum response factor in T cells by the viral oncoprotein tip.Cell Commun Signal. 2012 Mar 3;10(1):5. doi: 10.1186/1478-811X-10-5. Cell Commun Signal. 2012. PMID: 22385615 Free PMC article.
-
TNF-α Modulation of Intestinal Tight Junction Permeability Is Mediated by NIK/IKK-α Axis Activation of the Canonical NF-κB Pathway.Am J Pathol. 2016 May;186(5):1151-65. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2015.12.016. Epub 2016 Mar 4. Am J Pathol. 2016. PMID: 26948423 Free PMC article.
-
Roles for TNF-receptor associated factor 3 (TRAF3) in lymphocyte functions.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2014 Apr;25(2):147-56. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2013.12.002. Epub 2013 Dec 25. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2014. PMID: 24433987 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Collagen IV (COL4A1, COL4A2), a Component of the Viral Biofilm, Is Induced by the HTLV-1 Oncoprotein Tax and Impacts Virus Transmission.Front Microbiol. 2019 Oct 23;10:2439. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.02439. eCollection 2019. Front Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31708905 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

