Secretory mechanisms and intercellular transfer of microRNAs in living cells
- PMID: 20353945
- PMCID: PMC2878508
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.107821
Secretory mechanisms and intercellular transfer of microRNAs in living cells
Abstract
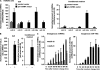
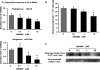
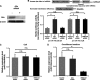
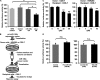
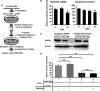
The existence of circulating microRNAs (miRNAs) in the blood of cancer patients has raised the possibility that miRNAs may serve as a novel diagnostic marker. However, the secretory mechanism and biological function of extracellular miRNAs remain unclear. Here, we show that miRNAs are released through a ceramide-dependent secretory machinery and that the secretory miRNAs are transferable and functional in the recipient cells. Ceramide, whose biosynthesis is regulated by neutral sphingomyelinase 2 (nSMase2), triggers secretion of small membrane vesicles called exosomes. The decreased activity of nSMase2 with a chemical inhibitor, GW4869, and a specific small interfering RNA resulted in the reduced secretion of miRNAs. Complementarily, overexpression of nSMase2 increased extracellular amounts of miRNAs. We also revealed that the endosomal sorting complex required for transport system is unnecessary for the release of miRNAs. Furthermore, a tumor-suppressive miRNA secreted via this pathway was transported between cells and exerted gene silencing in the recipient cells, thereby leading to cell growth inhibition. Our findings shed a ray of light on the physiological relevance of secretory miRNAs.
Figures
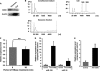

References
-
- Fleischhacker M., Schmidt B. (2007) Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1775, 181–232 - PubMed
-
- El-Hefnawy T., Raja S., Kelly L., Bigbee W. L., Kirkwood J. M., Luketich J. D., Godfrey T. E. (2004) Clin. Chem. 50, 564–573 - PubMed
-
- Tsui N. B., Ng E. K., Lo Y. M. (2002) Clin. Chem. 48, 1647–1653 - PubMed
-
- Hasselmann D. O., Rappl G., Tilgen W., Reinhold U. (2001) Clin. Chem. 47, 1488–1489 - PubMed
-
- Cocucci E., Racchetti G., Meldolesi J. (2009) Trends Cell Biol. 19, 43–51 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

