Expression of the homeobox genes OTX2 and OTX1 in the early developing human brain
- PMID: 20354145
- PMCID: PMC2889402
- DOI: 10.1369/jhc.2010.955757
Expression of the homeobox genes OTX2 and OTX1 in the early developing human brain
Abstract
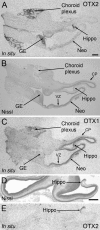
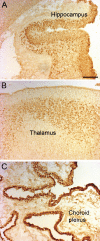
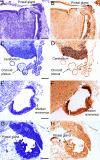
In rodents, the Otx2 gene is expressed in the diencephalon, mesencephalon, and cerebellum and is crucial for the development of these brain regions. Together with Otx1, Otx2 is known to cooperate with other genes to develop the caudal forebrain and, further, Otx1 is also involved in differentiation of young neurons of the deeper cortical layers. We have studied the spatial and temporal expression of the two homeobox genes OTX2 and OTX1 in human fetal brains from 7 to 14 weeks postconception by in situ hybridization and immunohistochemistry. OTX2 was expressed in the diencephalon, mesencephalon, and choroid plexus, with a minor expression in the basal telencephalon. The expression of OTX2 in the hippocampal anlage was strong, with no expression in the adjacent neocortex. Contrarily, the OTX1 expression was predominantly located in the proliferative zones of the neocortex. At later stages, the OTX2 protein was found in the subcommissural organ, pineal gland, and cerebellum. The early expression of OTX2 and OTX1 in proliferative cell layers of the human fetal brain supports the concept that these homeobox genes are important in neuronal cell development and differentiation: OTX1 primarily in the neocortex, and OTX2 in the archicortex, diencephalon, rostral brain stem, and cerebellum.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Otx2 and Otx1 protect diencephalon and mesencephalon from caudalization into metencephalon during early brain regionalization.Dev Biol. 2010 Nov 15;347(2):392-403. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2010.08.028. Epub 2010 Sep 16. Dev Biol. 2010. PMID: 20816794
-
Expression of the homeobox genes PAX6, OTX2, and OTX1 in the early human fetal retina.Int J Dev Neurosci. 2009 Aug;27(5):485-92. doi: 10.1016/j.ijdevneu.2009.04.004. Epub 2009 May 3. Int J Dev Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 19414065
-
Otx1 and Otx2 define layers and regions in developing cerebral cortex and cerebellum.J Neurosci. 1994 Oct;14(10):5725-40. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.14-10-05725.1994. J Neurosci. 1994. PMID: 7931541 Free PMC article.
-
Emx and Otx homeobox genes in the developing mouse brain.J Neurobiol. 1993 Oct;24(10):1356-66. doi: 10.1002/neu.480241008. J Neurobiol. 1993. PMID: 7901323 Review.
-
Emx and Otx gene expression in the developing mouse brain.Ciba Found Symp. 1995;193:100-16; discussion 117-26. doi: 10.1002/9780470514795.ch6. Ciba Found Symp. 1995. PMID: 8727489 Review.
Cited by
-
Novel mutations in PAX6, OTX2 and NDP in anophthalmia, microphthalmia and coloboma.Eur J Hum Genet. 2016 Apr;24(4):535-41. doi: 10.1038/ejhg.2015.155. Epub 2015 Jul 1. Eur J Hum Genet. 2016. PMID: 26130484 Free PMC article.
-
PCR Strategies for Complete Allele Calling in Multigene Families Using High-Throughput Sequencing Approaches.PLoS One. 2016 Jun 13;11(6):e0157402. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0157402. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27294261 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of a 5-Gene Signature Predicting Progression and Prognosis of Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma.Med Sci Monit. 2019 Jun 13;25:4401-4413. doi: 10.12659/MSM.917399. Med Sci Monit. 2019. PMID: 31194719 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in Otx2 and parvalbumin immunoreactivity in the superior colliculus in the platelet-derived growth factor receptor-β knockout mice.Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013:848265. doi: 10.1155/2013/848265. Epub 2013 Nov 11. Biomed Res Int. 2013. PMID: 24319691 Free PMC article.
-
Common microRNA-mRNA interactions exist among distinct porcine iPSC lines independent of their metastable pluripotent states.Cell Death Dis. 2017 Aug 31;8(8):e3027. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2017.426. Cell Death Dis. 2017. PMID: 29048434 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Acampora D, Mazan S, Avantaggiato V, Barone P, Tuorto F, Lallemand Y, Brûlet P, et al. (1996) Epilepsy and brain abnormalities in mice lacking the Otx1 gene. Nat Genet 14:218–222 - PubMed
-
- Acampora D, Mazan S, Lallemand Y, Avantaggiato V, Maury M, Simeone A, Brûlet P (1995) Forebrain and midbrain regions are deleted in Otx2−/− mutants due to a defective anterior neuroectoderm specification during gastrulation. Development 121:3279–3290 - PubMed
-
- Altman PL, Dittmer DS (1962) Growth, Including Reproduction and Morphological Development. Washington, Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology
-
- Ando K, Yagi H, Suda Y, Aizawa S, Sakashita M, Nagano T, Terashima T, et al. (2008) Establishment of framework of the cortical area is influenced by Otx1. Neurosci Res 60:457–459 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

