Diffusion weighted imaging in the liver
- PMID: 20355235
- PMCID: PMC2848365
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i13.1567
Diffusion weighted imaging in the liver
Abstract
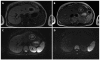
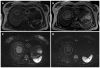
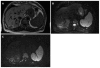
Diffusion weighted magnetic resonance imaging (DWI) is an imaging technique which provides tissue contrast by the measurement of diffusion properties of water molecules within tissues. Diffusion is expressed in an apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC), which reflects the diffusion properties unique to each type of tissue. DWI has been originally used in neuroradiology. More recently, DWI has increasingly been used in addition to conventional unenhanced and enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in other parts of the body. The reason for this delay was a number of technical problems inherent to the technique, making DWI very sensitive to artifacts, which had to be overcome. With assessment of ADC values, DWI proved to be helpful in characterization of focal liver lesions. However, DWI should always be used in conjunction to conventional MRI since there is considerable overlap between ADC values of benign and malignant lesions. DWI is useful in the detection of hepatocellular carcinoma in the cirrhotic liver and detection of liver metastases in oncological patients. In addition, DWI is a promising tool in the prediction of tumor responsiveness to chemotherapy and the follow-up of oncological patients after treatment, as DWI may be capable of detecting recurrent disease earlier than conventional imaging. This review focuses on the most common applications of DWI in the liver.
Figures
References
-
- Bammer R. Basic principles of diffusion-weighted imaging. Eur J Radiol. 2003;45:169–184. - PubMed
-
- Naganawa S, Kawai H, Fukatsu H, Sakurai Y, Aoki I, Miura S, Mimura T, Kanazawa H, Ishigaki T. Diffusion-weighted imaging of the liver: technical challenges and prospects for the future. Magn Reson Med Sci. 2005;4:175–186. - PubMed
-
- Thoeny HC, De Keyzer F. Extracranial applications of diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging. Eur Radiol. 2007;17:1385–1393. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

