Effects of thymidine phosphorylase on tumor aggressiveness and 5-fluorouracil sensitivity in cholangiocarcinoma
- PMID: 20355241
- PMCID: PMC2848371
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i13.1631
Effects of thymidine phosphorylase on tumor aggressiveness and 5-fluorouracil sensitivity in cholangiocarcinoma
Abstract
Aim: To evaluate the role of thymidine phosphorylase (TP) in cholangiocarcinoma using small interfering RNA (siRNA).
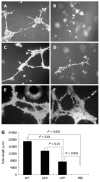
Methods: A human cholangiocarcinoma-derived cell line KKU-M139, which has a naturally high level of endogenous TP, had TP expression transiently knocked down using siRNA. Cell growth, migration, in vitro angiogenesis, apoptosis, and cytotoxicity were assayed in TP knockdown and wild-type cell lines.
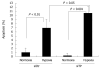
Results: TP mRNA and protein expression were decreased by 87.1% + or - 0.49% and 72.5% + or - 3.2%, respectively, compared with control cells. Inhibition of TP significantly decreased migration of KKU-M139, and suppressed migration and tube formation of human umbilical vein endothelial cells. siRNA also reduced the ability of TP to resist hypoxia-induced apoptosis, while suppression of TP reduced the sensitivity of KKU-M139 to 5-fluorouracil.
Conclusion: Inhibition of TP may be beneficial in decreasing angiogenesis-dependent growth and migration of cholangiocarcinoma but may diminish the response to 5-fluorouracil chemotherapy.
Figures


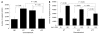

Similar articles
-
Thymidine phosphorylase promotes angiogenesis and tumour growth in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma.Cell Biochem Funct. 2020 Aug;38(6):743-752. doi: 10.1002/cbf.3541. Epub 2020 May 31. Cell Biochem Funct. 2020. PMID: 32476180
-
Blockage of 2-deoxy-D-ribose-induced angiogenesis with rapamycin counteracts a thymidine phosphorylase-based escape mechanism available for colon cancer under 5-fluorouracil therapy.Clin Cancer Res. 2004 Mar 1;10(5):1843-52. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-1176-3. Clin Cancer Res. 2004. PMID: 15014039
-
Thymosin β10 as a predictive biomarker of response to 5-fluorouracil chemotherapy in cholangiocarcinoma.Ann Hepatol. 2016 Jul-Aug;15(4):577-85. Ann Hepatol. 2016. PMID: 27236157
-
Making capecitabine targeted therapy for breast cancer: which is the role of thymidine phosphorylase?Clin Breast Cancer. 2013 Jun;13(3):167-72. doi: 10.1016/j.clbc.2012.10.002. Epub 2012 Dec 5. Clin Breast Cancer. 2013. PMID: 23218471 Review.
-
Multifunctional role of thymidine phosphorylase in cancer.Trends Cancer. 2022 Jun;8(6):482-493. doi: 10.1016/j.trecan.2022.01.018. Epub 2022 Feb 19. Trends Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35193822 Review.
Cited by
-
MDACT: A New Principle of Adjunctive Cancer Treatment Using Combinations of Multiple Repurposed Drugs, with an Example Regimen.Cancers (Basel). 2022 May 23;14(10):2563. doi: 10.3390/cancers14102563. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35626167 Free PMC article.
-
Mass spectrometry-based analysis of formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded distal cholangiocarcinoma identifies stromal thrombospondin-2 as a potential prognostic marker.J Transl Med. 2020 Sep 4;18(1):343. doi: 10.1186/s12967-020-02498-3. J Transl Med. 2020. PMID: 32887625 Free PMC article.
-
ERCC1 Can Be a Prognostic Factor in Hilar Cholangiocarcinoma and Extrahepatic Bile Duct Cancer, But Not in Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma.Cancer Res Treat. 2013 Mar;45(1):63-9. doi: 10.4143/crt.2013.45.1.63. Epub 2013 Mar 31. Cancer Res Treat. 2013. PMID: 23613672 Free PMC article.
-
Vorinostat synergises with capecitabine through upregulation of thymidine phosphorylase.Br J Cancer. 2010 Nov 23;103(11):1680-91. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6605969. Epub 2010 Nov 2. Br J Cancer. 2010. PMID: 21045833 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical significance of the thymidylate synthase, dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase, and thymidine phosphorylase mRNA expressions in hepatocellular carcinoma patients receiving 5-fluorouracil-based transarterial chemoembolization treatment.Onco Targets Ther. 2013 Jul 3;6:811-8. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S46498. Print 2013. Onco Targets Ther. 2013. PMID: 23861589 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vatanasapt V, Sriamporn S, Vatanasapt P. Cancer control in Thailand. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2002;32 Suppl:S82–S91. - PubMed
-
- Uttaravichien T, Bhudhisawasdi V, Pairojkul C, Pugkhem A. Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma in Thailand. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 1999;6:128–135. - PubMed
-
- Horie S, Endo K, Kawasaki H, Terada T. Overexpression of MDM2 protein in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: relationship with p53 overexpression, Ki-67 labeling, and clinicopathological features. Virchows Arch. 2000;437:25–30. - PubMed
-
- Limpaiboon T, Khaenam P, Chinnasri P, Soonklang M, Jearanaikoon P, Sripa B, Pairojkul C, Bhudhisawasdi V. Promoter hypermethylation is a major event of hMLH1 gene inactivation in liver fluke related cholangiocarcinoma. Cancer Lett. 2005;217:213–219. - PubMed
-
- Limpaiboon T, Krissadarak K, Sripa B, Jearanaikoon P, Bhuhisawasdi V, Chau-in S, Romphruk A, Pairojkul C. Microsatellite alterations in liver fluke related cholangiocarcinoma are associated with poor prognosis. Cancer Lett. 2002;181:215–222. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

