Upper gastrointestinal hemorrhage caused by superwarfarin poisoning
- PMID: 20355251
- PMCID: PMC2848381
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i13.1680
Upper gastrointestinal hemorrhage caused by superwarfarin poisoning
Abstract
Superwarfarins are a class of rodenticides. Gastrointestinal hemorrhage is a fatal complication of superwarfarin poisoning, requiring immediate treatment. Here, we report a 55-year-old woman with tardive upper gastrointestinal hemorrhage caused by superwarfarin poisoning after endoscopic cold mucosal biopsy.
Figures


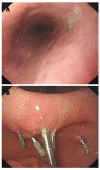
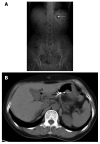
Similar articles
-
Prolonged coagulopathy related to coumarin rodenticide in a young patient: superwarfarin poisoning.Cardiovasc J Afr. 2012 Oct 23;23(9):e9-e11. doi: 10.5830/CVJA-2012-051. Cardiovasc J Afr. 2012. PMID: 23108575
-
Intracerebellar hemorrhage caused by superwarfarin poisoning.Neurol Sci. 2013 Nov;34(11):2071-2. doi: 10.1007/s10072-013-1445-2. Epub 2013 Apr 18. Neurol Sci. 2013. PMID: 23595548 No abstract available.
-
Superwarfarin (brodifacoum) poisoning.Anaesth Intensive Care. 1997 Dec;25(6):707-9. doi: 10.1177/0310057X9702500622. Anaesth Intensive Care. 1997. PMID: 9452861
-
Superwarfarin poisoning.J Emerg Med. 1989 Nov-Dec;7(6):627-31. doi: 10.1016/0736-4679(89)90010-3. J Emerg Med. 1989. PMID: 2696752 Review.
-
A case of bromadiolone (superwarfarin) ingestion.CMAJ. 1992 Jul 1;147(1):60-2. CMAJ. 1992. PMID: 1393889 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Suicide following acute admissions for physical illnesses across England and Wales.Psychol Med. 2018 Mar;48(4):578-591. doi: 10.1017/S0033291717001787. Epub 2017 Jul 17. Psychol Med. 2018. PMID: 28714426 Free PMC article.
-
A guide to acquired vitamin K coagulophathy diagnosis and treatment: the Russian perspective.Daru. 2017 Apr 17;25(1):10. doi: 10.1186/s40199-017-0175-z. Daru. 2017. PMID: 28416008 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Laposata M, Van Cott EM, Lev MH. Case records of the Massachusetts General Hospital. Case 1-2007. A 40-year-old woman with epistaxis, hematemesis, and altered mental status. N Engl J Med. 2007;356:174–182. - PubMed
-
- Pavlu J, Harrington DJ, Voong K, Savidge GF, Jan-Mohamed R, Kaczmarski R. Superwarfarin poisoning. Lancet. 2005;365:628. - PubMed
-
- Bruno GR, Howland MA, McMeeking A, Hoffman RS. Long-acting anticoagulant overdose: brodifacoum kinetics and optimal vitamin K dosing. Ann Emerg Med. 2000;36:262–267. - PubMed
-
- Chua JD, Friedenberg WR. Superwarfarin poisoning. Arch Intern Med. 1998;158:1929–1932. - PubMed
-
- Watson WA, Litovitz TL, Rodgers GC Jr, Klein-Schwartz W, Reid N, Youniss J, Flanagan A, Wruk KM. 2004 Annual report of the American Association of Poison Control Centers Toxic Exposure Surveillance System. Am J Emerg Med. 2005;23:589–666. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

