Stable, ligand-doped, poly(bis-SorbPC) lipid bilayer arrays for protein binding and detection
- PMID: 20355927
- PMCID: PMC2857382
- DOI: 10.1021/am900177p
Stable, ligand-doped, poly(bis-SorbPC) lipid bilayer arrays for protein binding and detection
Abstract
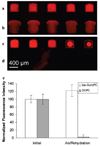
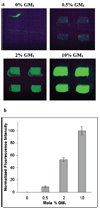
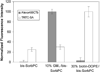
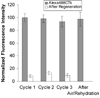
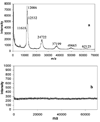
A continuous-flow microspotter was used to generate planar arrays of stabilized bilayers composed of the polymerizable lipid bis-SorbPC and dopant lipids bearing ligands for proteins. Fluorescence microscopy was used to determine the uniformity of the bilayers and to detect protein binding. After UV-initiated polymerization, poly(lipid) bilayer microarrays were air-stable. Cholera toxin subunit b (CTb) bound to an array of poly(lipid) bilayers doped with GM(1), and the extent of binding was correlated to the mole percentage of GM(1) in each spot. A poly(lipid) bilayer array composed of spots doped with GM(1) and spots doped with biotin-DOPE specifically bound CTb and streptavidin to the respective spots from a dissolved mixture of the two proteins. Poly(bis-SorbPC)/GM(1) arrays retained specific CTb binding capacity after multiple regenerations with a protein denaturing solution and also after exposure to air. In addition, these arrays are stable in vacuum, which allows the use of MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry to detect specifically bound CTb. This work demonstrates the considerable potential of poly(lipid) bilayer arrays for high-throughput binding assays and lipidomics studies.
Figures
References
-
- Muller UR, Nicolau DV, editors. Microarray Technology and Its Applications. Berlin: Springer; 2005.
-
- Stoll D, Templin M, Bachmann J, Thomas Joos T. Microsystems. 2006;16:245–267.
-
- Chen T. Infect. Disord.: Drug Targets. 2006;6:263–279. - PubMed
-
- Park S, Lee MR, Shin I. Chem. Commun. 2008:4389–4399. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

