Immobilizing enzymes onto electrode arrays by hydrogel photolithography to fabricate multi-analyte electrochemical biosensors
- PMID: 20356276
- PMCID: PMC2849179
- DOI: 10.1021/am9007819
Immobilizing enzymes onto electrode arrays by hydrogel photolithography to fabricate multi-analyte electrochemical biosensors
Abstract
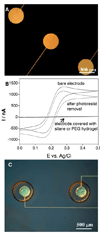
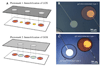
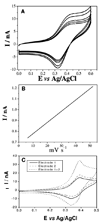
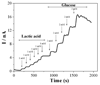
This paper describes a biomaterial microfabrication approach for interfacing functional biomolecules (enzymes) with electrode arrays. Poly (ethylene glycol) (PEG) hydrogel photopatterning was employed to integrate gold electrode arrays with the enzymes glucose oxidase (GOX) and lactate oxidase (LOX). In this process, PEG diacrylate (DA)-based prepolymer containing enzyme molecules as well as redox species (vinylferrocene) was spin-coated, registered, and UV cross-linked on top of an array of gold electrodes. As a result, enzyme-carrying circular hydrogel structures (600 microm diameter) were fabricated on top of 300 microm diameter gold electrodes. Importantly, when used with multiple masks, hydrogel photolithography allowed us to immobilize GOX and LOX molecules on adjacent electrodes within the same electrode array. Cyclic voltammetry and amperometry were used to characterize biosensor electrode arrays. The response of the biosensor array was linear for up to 20 mM glucose with sensitivity of 0.9 microA cm(-2) mM(-1) and 10 mM lactate with sensitivity of 1.1 microA cm(-2) mM(-1). Importantly, simultaneous detection of glucose and lactate from the same electrode array was demonstrated. A novel strategy for integrating biological and electrical components of a biosensor described in this paper provides the flexibility to spatially resolve and register different biorecognition elements with individual members of a miniature electrode array. Of particular interest to us are future applications of these miniature electrodes for real-time monitoring of metabolite fluxes in the vicinity of living cells.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Chitosan coated on the layers' glucose oxidase immobilized on cysteamine/Au electrode for use as glucose biosensor.Biosens Bioelectron. 2014 Oct 15;60:271-6. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2014.04.035. Epub 2014 Apr 30. Biosens Bioelectron. 2014. PMID: 24820862
-
Electrochemical biosensing platforms using poly-cyclodextrin and carbon nanotube composite.Biosens Bioelectron. 2010 Sep 15;26(1):295-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2010.06.036. Epub 2010 Jun 30. Biosens Bioelectron. 2010. PMID: 20655192
-
Microfluidic bioassay system based on microarrays of hydrogel sensing elements entrapping quantum dot-enzyme conjugates.Biosens Bioelectron. 2012 Jan 15;31(1):529-36. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2011.11.033. Epub 2011 Nov 28. Biosens Bioelectron. 2012. PMID: 22177543
-
Carbon nanotubes-nanoflake-like SnS2 nanocomposite for direct electrochemistry of glucose oxidase and glucose sensing.Biosens Bioelectron. 2013 Mar 15;41:698-703. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2012.09.059. Epub 2012 Oct 4. Biosens Bioelectron. 2013. PMID: 23083908
-
Hard and soft micro- and nanofabrication: An integrated approach to hydrogel-based biosensing and drug delivery.J Control Release. 2010 Feb 15;141(3):303-13. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2009.12.012. Epub 2009 Dec 24. J Control Release. 2010. PMID: 20036310 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Realizing new designs of multiplexed electrode chips by 3-D printed masks.RSC Adv. 2021 Jun 17;11(35):21600-21606. doi: 10.1039/d1ra03482k. eCollection 2021 Jun 15. RSC Adv. 2021. PMID: 35478805 Free PMC article.
-
Electrochemical biosensors for on-chip detection of oxidative stress from immune cells.Biomicrofluidics. 2011 Sep;5(3):32008-3200811. doi: 10.1063/1.3624739. Epub 2011 Sep 20. Biomicrofluidics. 2011. PMID: 22007269 Free PMC article.
-
Micropatterned surfaces functionalized with electroactive peptides for detecting protease release from cells.Anal Chem. 2013 Jan 2;85(1):220-7. doi: 10.1021/ac302547p. Epub 2012 Dec 14. Anal Chem. 2013. PMID: 23181468 Free PMC article.
-
Micropatterned sensing hydrogels integrated with reconfigurable microfluidics for detecting protease release from cells.Anal Chem. 2013 Dec 17;85(24):11893-901. doi: 10.1021/ac402660z. Epub 2013 Nov 26. Anal Chem. 2013. PMID: 24255999 Free PMC article.
-
Microfluidic impact printer with interchangeable cartridges for versatile non-contact multiplexed micropatterning.Lab Chip. 2013 May 21;13(10):1902-10. doi: 10.1039/c3lc41372a. Epub 2013 Mar 25. Lab Chip. 2013. PMID: 23525299 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Updike SJ, Hicks GP. Nature. 1967;214:986. - PubMed
-
- Pishko MV, Michael AC, Heller A. Anal. Chem. 1991;63:2268–2272. - PubMed
-
- Quinn CP, Pishko MV, Schmidtke DW, Ishikawa M, Wagner JG, Raskin P, Hubbell JA, Heller A. Am. J. Physiol. 1995;269:E155. - PubMed
-
- Ohara TJ, Rajagopalan R, Heller A. Anal. Chem. 1994;66:2451–2457. - PubMed
-
- Hu Y, Zhang Y, Wilson GS. Anal. Chim. Acta. 1993;1993:503–511.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

