Changes of tau profiles in brains of the hamsters infected with scrapie strains 263 K or 139 A possibly associated with the alteration of phosphate kinases
- PMID: 20356412
- PMCID: PMC2868850
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2334-10-86
Changes of tau profiles in brains of the hamsters infected with scrapie strains 263 K or 139 A possibly associated with the alteration of phosphate kinases
Abstract
Background: Phospho-tau deposition has been described in a rare genetic human prion disease, Gerstmann-Sträussler-Scheinker syndrome, but is not common neuropathological picture for other human and animal transmissible spongiform encephalopathies (TSEs). This study investigated the possible changes of tau and phosphorylated tau (p-tau, at Ser396, Ser404, and Ser202/Thr205) in scrapie experimental animals.
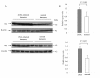
Methods: The profiles of tau and p-tau (p-tau, at Ser396, Ser404, and Ser202/Thr205) in the brain tissues of agents 263K- or 139A-infected hamsters were evaluated by Western blots and real-time PCR. Meanwhile, the transcriptional and expressive levels of GSK3beta and CDK5 in the brains were tested.
Results: The contents of total tau and p-tau at Ser202/Thr205 increased, but p-tau at Ser396 and Ser404 decreased at the terminal stages, regardless of scrapie strains. Transcriptional levels of two tau isoforms were also increased. Additionally, it showed higher CDK5, but lower GSK3beta transcriptional and expressive levels in the brains of scrapie-infected animals. Analysis of brain samples collected from different times after inoculated with agent 263 K revealed that the changes of tau profiles and phosphate kinases were time-relative events.
Conclusion: These data suggest that changes of profiles of p-tau at Ser396, Ser404 and Ser202/Thr205 are illness-correlative phenomena in TSEs, which may arise of the alteration of phosphate kinases. Alteration of tau, p-tau (Ser396, Ser404, and Ser202/Thr205), GSK3beta and CDK5 were either intermediate or consequent events in TSE pathogenesis and proposed the potential linkage of these bioactive proteins with the pathogenesis of prion diseases.
Figures

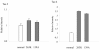



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

