Crystal structure of HLA-DP2 and implications for chronic beryllium disease
- PMID: 20356827
- PMCID: PMC2867715
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1001772107
Crystal structure of HLA-DP2 and implications for chronic beryllium disease
Abstract
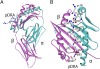
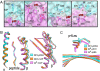
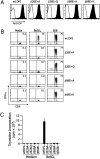
Chronic beryllium disease (CBD) is a fibrotic lung disorder caused by beryllium (Be) exposure and is characterized by granulomatous inflammation and the accumulation of Be-responsive CD4(+) T cells in the lung. Genetic susceptibility to CBD has been associated with certain alleles of the MHCII molecule HLA-DP, especially HLA-DPB1*0201 and other alleles that contain a glutamic acid residue at position 69 of the beta-chain (betaGlu69). The HLA-DP alleles that can present Be to T cells match those implicated in the genetic susceptibility, suggesting that the HLA contribution to disease is based on the ability of those molecules to bind and present Be to T cells. The structure of HLA-DP2 and its interaction with Be are unknown. Here, we present the HLA-DP2 structure with its antigen-binding groove occupied by a self-peptide derived from the HLA-DR alpha-chain. The most striking feature of the structure is an unusual solvent exposed acidic pocket formed between the peptide backbone and the HLA-DP2 beta-chain alpha-helix and containing three glutamic acids from the beta-chain, including betaGlu69. In the crystal packing, this pocket has been filled with the guanidinium group of an arginine from a neighboring molecule. This positively charged moiety forms an extensive H-bond/salt bridge network with the three glutamic acids, offering a plausible model for how Be-containing complexes might occupy this site. This idea is strengthened by the demonstration that mutation of any of the three glutamic acids in this pocket results in loss of the ability of DP2 to present Be to T cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Jones EY, Fugger L, Strominger JL, Siebold C. MHC class II proteins and disease: A structural perspective. Nat Rev Immunol. 2006;6:271–282. - PubMed
-
- Nepom GT. Major histocompatibility complex-directed susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis. Adv Immunol. 1998;68:315–332. - PubMed
-
- Nepom GT, Erlich H. MHC class-II molecules and autoimmunity. Annu Rev Immunol. 1991;9:493–525. - PubMed
-
- Dong RP, et al. HLA-A and DPB1 loci confer susceptibility to Graves’ disease. Hum Immunol. 1992;35:165–172. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
- R01 AI018785/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01 ES011810/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- AI18785/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- T32 AI007405/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- HL62410/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K24 HL102245/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI017134/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AI018785/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AI018785/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI022295/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL062410/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- ES11810/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AI017134/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI17134/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

