Thrombin and collagen induce a feedback inhibitory signaling pathway in platelets involving dissociation of the catalytic subunit of protein kinase A from an NFkappaB-IkappaB complex
- PMID: 20356841
- PMCID: PMC2881761
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.077602
Thrombin and collagen induce a feedback inhibitory signaling pathway in platelets involving dissociation of the catalytic subunit of protein kinase A from an NFkappaB-IkappaB complex
Abstract
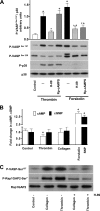
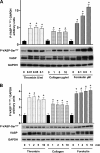
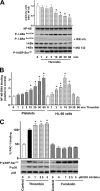
Protein kinase A (PKA) activation by cAMP phosphorylates multiple target proteins in numerous platelet inhibitory pathways that have a very important role in maintaining circulating platelets in a resting state. Here we show that in thrombin- and collagen-stimulated platelets, PKA is activated by cAMP-independent mechanisms involving dissociation of the catalytic subunit of PKA (PKAc) from an NFkappaB-IkappaBalpha-PKAc complex. We demonstrate mRNA and protein expression for most of the NFkappaB family members in platelets. From resting platelets, PKAc was co-immunoprecipitated with IkappaBalpha, and conversely, IkappaBalpha was also co-immunoprecipitated with PKAc. This interaction was significantly reduced in thrombin- and collagen-stimulated platelets. Stimulation of platelets with thrombin- or collagen-activated IKK, at least partly by PI3 kinase-dependent pathways, leading to phosphorylation of IkappaBalpha, disruption of an IkappaBalpha-PKAc complex, and release of free, active PKAc, which phosphorylated VASP and other PKA substrates. IKK inhibitor inhibited thrombin-stimulated IkBalpha phosphorylation, PKA-IkBalpha dissociation, and VASP phosphorylation, and potentiated integrin alphaIIbbeta3 activation and the early phase of platelet aggregation. We conclude that thrombin and collagen not only cause platelet activation but also appear to fine-tune this response by initiating downstream NFkappaB-dependent PKAc activation, as a novel feedback inhibitory signaling mechanism for preventing undesired platelet activation.
Figures





Similar articles
-
A noble function of BAY 11-7082: Inhibition of platelet aggregation mediated by an elevated cAMP-induced VASP, and decreased ERK2/JNK1 phosphorylations.Eur J Pharmacol. 2010 Feb 10;627(1-3):85-91. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2009.11.005. Epub 2009 Nov 10. Eur J Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 19913011
-
Requirement of thyrotropin-dependent complex formation of protein kinase A catalytic subunit with inhibitor of {kappa}B proteins for activation of p65 nuclear factor-{kappa}B by tumor necrosis factor-{alpha}.Endocrinology. 2005 Apr;146(4):1999-2005. doi: 10.1210/en.2004-1178. Epub 2005 Jan 6. Endocrinology. 2005. PMID: 15637292
-
cAMP- and cGMP-elevating agents inhibit GPIbα-mediated aggregation but not GPIbα-stimulated Syk activation in human platelets.Cell Commun Signal. 2019 Sep 13;17(1):122. doi: 10.1186/s12964-019-0428-1. Cell Commun Signal. 2019. PMID: 31519182 Free PMC article.
-
A most versatile kinase: The catalytic subunit of PKA in T-cell biology.Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2021;361:301-318. doi: 10.1016/bs.ircmb.2021.01.005. Epub 2021 Jan 27. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 34074497 Review.
-
Nuclear emancipation: a platelet tour de force.Sci Signal. 2010 Oct 19;3(144):pe37. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.3144pe37. Sci Signal. 2010. PMID: 20959522 Review.
Cited by
-
Lack of effect of ODQ does not exclude cGMP signalling via NO-sensitive guanylyl cyclase.Br J Pharmacol. 2013 Sep;170(2):317-27. doi: 10.1111/bph.12275. Br J Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23763290 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of Human Platelet Activation and Prevention of Arterial Thrombosis in Mice by Auraptene through Inhibition of NF-κB Pathway.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jul 7;21(13):4810. doi: 10.3390/ijms21134810. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32646046 Free PMC article.
-
Role of NF-κB in Platelet Function.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Aug 27;20(17):4185. doi: 10.3390/ijms20174185. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31461836 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Platelet microRNA-mRNA coexpression profiles correlate with platelet reactivity.Blood. 2011 May 12;117(19):5189-97. doi: 10.1182/blood-2010-09-299719. Epub 2011 Mar 17. Blood. 2011. PMID: 21415270 Free PMC article.
-
Platelets as Mediators of Neuroinflammation and Thrombosis.Front Immunol. 2020 Oct 6;11:548631. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.548631. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 33123127 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Italiano J. E., Jr., Patel-Hett S., Hartwig J. H. (2007) J. Thromb. Haemost. 5, Suppl. 1, 18–23 - PubMed
-
- Junt T., Schulze H., Chen Z., Massberg S., Goerge T., Krueger A., Wagner D. D., Graf T., Italiano J. E., Jr., Shivdasani R. A., von Andrian U. H. (2007) Science 317, 1767–1770 - PubMed
-
- Ruggeri Z. M., Mendolicchio G. L. (2007) Circ. Res. 100, 1673–1685 - PubMed
-
- Davì G., Patrono C. (2007) N. Engl. J. Med. 357, 2482–2494 - PubMed
-
- Varga-Szabo D., Pleines I., Nieswandt B. (2008) Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 28, 403–412 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

