Kruppel-like factor 4 inhibits epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition through regulation of E-cadherin gene expression
- PMID: 20356845
- PMCID: PMC2878056
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.114546
Kruppel-like factor 4 inhibits epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition through regulation of E-cadherin gene expression
Abstract
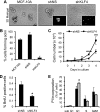
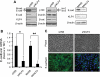
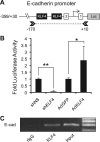
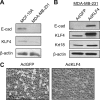
The Krüppel-like factor 4 (KLF4) is a transcriptional regulator of proliferation and differentiation in epithelial cells, both during development and tumorigenesis. Although KLF4 functions as a tumor suppressor in several tissues, including the colon, the role of KLF4 in breast cancer is less clear. Here, we show that KLF4 is necessary for maintenance of the epithelial phenotype in non-transformed MCF-10A mammary epithelial cells. KLF4 silencing led to alterations in epithelial cell morphology and migration, indicative of an epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Consistent with these changes, decreased levels of KLF4 also resulted in the loss of E-cadherin protein and mRNA. Promoter/reporter analyses revealed decreased E-cadherin promoter activity with KLF4 silencing, while chromatin immunoprecipitation identified endogenous KLF4 binding to the GC-rich/E-box region of this promoter. Furthermore, forced expression of KLF4 in the highly metastatic MDA-MB-231 breast tumor cell line was sufficient to restore E-cadherin expression and suppress migration and invasion. These findings identify E-cadherin as a novel transcriptional target of KLF4. The clear requirement for KLF4 to maintain E-cadherin expression and prevent epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in mammary epithelial cells supports a metastasis suppressive role for KLF4 in breast cancer.
Figures

References
-
- Segre J. A., Bauer C., Fuchs E. (1999) Nat. Genet. 22, 356–360 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

