A rift between implicit and explicit conditioned valence in human pain relief learning
- PMID: 20356893
- PMCID: PMC2894900
- DOI: 10.1098/rspb.2010.0103
A rift between implicit and explicit conditioned valence in human pain relief learning
Abstract
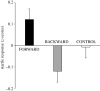
Pain is aversive, but does the cessation of pain ('relief') have a reward-like effect? Indeed, fruitflies avoid an odour previously presented before a painful event, but approach an odour previously presented after a painful event. Thus, event-timing may turn punishment to reward. However, is event-timing also crucial in humans who can have explicit cognitions about associations? Here, we show that stimuli associated with pain-relief acquire positive implicit valence but are explicitly rated as aversive. Specifically, the startle response, an evolutionarily conserved defence reflex, is attenuated by stimuli that had previously followed a painful event, indicating implicit positive valence of the conditioned stimulus; nevertheless, participants explicitly evaluate these stimuli as 'emotionally negative'. These results demonstrate a rift between the implicit and explicit conditioned valence induced by pain relief. They might explain why humans in some cases are attracted by conditioned stimuli despite explicitly judging them as negative.
Figures
References
-
- Abbott L. F., Nelson S. B.2000Synaptic plasticity: taming the beast. Nat. Neurosci. 3, 1178–1183 (doi:10.1038/81453) - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bechara A.2005Decision making, impulse control and loss of willpower to resist drugs: a neurocognitive perspective. Nat. Neurosci. 8, 1458–1463 (doi:10.1038/nn1584) - DOI - PubMed
-
- Blumenthal T. D., Cuthbert B. N., Filion D. L., Hackley S., Lipp O. V., Van Boxtel A.2005Committee report: guidelines for human startle eyeblink electromyographic studies. Psychophysiology 42, 1–15 (doi:10.1111/j.1469-8986.2005.00271.x) - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bouton M. E., Barlow D. H., Mineka S.2001A modern learning theory perspective on the etiology of panic disorder. Psychol. Rev. 108, 4–32 (doi:10.1037/0033-295X.108.1.4) - DOI - PubMed
-
- Brischoux F., Chakraborty S., Brierley D. I., Ungless M. A.2009Phasic excitation of dopamine neurons in ventral VTA by noxious stimuli. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. 106, 4894–4899 (doi:10.1073/pnas.0811507106) - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

