Detection of Latin American strains of Histoplasma in a murine model by use of a commercially available antigen test
- PMID: 20357054
- PMCID: PMC2863395
- DOI: 10.1128/CVI.00043-10
Detection of Latin American strains of Histoplasma in a murine model by use of a commercially available antigen test
Abstract
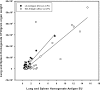
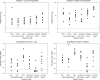
During a Histoplasma outbreak in a colony of fruit bats at a southern United States zoo, it was observed that although Histoplasma was recovered in culture from multiple sites at necropsy, none of the samples collected from those bats tested positive for Histoplasma antigen (HAg). Five of the Histoplasma isolates from the bats were subsequently identified as Latin American (LA) clade A, restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) class 6. These observations raised concern as to whether the commercially available HAg test could detect Histoplasma antigen not of the North American clade upon which the HAg test had been developed. To evaluate this concern, a murine model of disseminated histoplasmosis was established, and mice were infected with multiple LA Histoplasma isolates, including clinical isolates recovered from Brazilian AIDS patients (RFLP class 5 and class 6) and isolates recovered from the bats during the outbreak (RFLP class 6). Histoplasma antigen was detected in all infected mice in our experiments, even when Histoplasma was not recovered in culture. Because the currently available HAg test is able to detect Histoplasma antigen in mice infected with Latin American isolates, this suggests that bat host factors rather than differences among Histoplasma RFLP classes were responsible for the inability to detect HAg in infected bats.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Detection of Histoplasma capsulatum antigen in Panamanian patients with disseminated histoplasmosis and AIDS.Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2008 Apr;15(4):681-3. doi: 10.1128/CVI.00358-07. Epub 2008 Feb 20. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18287576 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical evaluation of urine Histoplasma capsulatum antigen measurement in cats with suspected disseminated histoplasmosis.J Feline Med Surg. 2012 Aug;14(8):512-5. doi: 10.1177/1098612X12450121. Epub 2012 May 24. J Feline Med Surg. 2012. PMID: 22628269 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular detection of Histoplasma capsulatum in bats of the Amazon biome in Pará state, Brazil.Transbound Emerg Dis. 2021 Mar;68(2):758-766. doi: 10.1111/tbed.13740. Epub 2020 Aug 4. Transbound Emerg Dis. 2021. PMID: 32686315
-
The role of bats in the propagation and spread of histoplasmosis: a review.J Wildl Dis. 1981 Apr;17(2):191-6. doi: 10.7589/0090-3558-17.2.191. J Wildl Dis. 1981. PMID: 7017172 Review. No abstract available.
-
Infection of bats with Histoplasma species.Med Mycol. 2023 Aug 2;61(8):myad080. doi: 10.1093/mmy/myad080. Med Mycol. 2023. PMID: 37553137 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Blastomyces dermatitidis Yeast Lysate Antigen Combinations: Antibody Detection in Dogs with Blastomycosis.Vet Med Int. 2013;2013:940126. doi: 10.1155/2013/940126. Epub 2013 Oct 8. Vet Med Int. 2013. PMID: 24236239 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic accuracy cohort study and clinical value of the Histoplasma urine antigen (ALPHA Histoplasma EIA) for disseminated histoplasmosis among HIV infected patients: A multicenter study.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2018 Nov 5;12(11):e0006872. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0006872. eCollection 2018 Nov. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2018. PMID: 30395572 Free PMC article.
-
Detection of Histoplasma capsulatum antigen in Panamanian patients with disseminated histoplasmosis and AIDS.Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2008 Apr;15(4):681-3. doi: 10.1128/CVI.00358-07. Epub 2008 Feb 20. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18287576 Free PMC article.
-
Bat-associated microbes: Opportunities and perils, an overview.Heliyon. 2023 Nov 18;9(12):e22351. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e22351. eCollection 2023 Dec. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 38125540 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Connolly, P., J. Wheat, C. Schnizlein-Bick, M. Durkin, S. Kohler, M. Smedema, E. Brizendine, R. Hector, and D. Loebenberg. 1999. Comparison of a new triazole antifungal agent, Schering 56592, with itraconazole and amphotericin B for treatment of histoplasmosis in immunocompetent mice. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 43:322-328. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Durkin, M., P. Connolly, K. Karimi, E. Wheat, C. Schnizlein-Bick, S. D. Allen, K. Alves, R. P. Tewari, and E. Keath. 2004. Pathogenic differences between North American and Latin American strains of Histoplasma capsulatum var. capsulatum in experimentally infected mice. J. Clin. Microbiol. 42:4370-4373. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Greer, D. L., and D. N. McMurray. 1981. Pathogenesis of experimental histoplasmosis in the bat, Artibeus lituratus. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 30:653-659. - PubMed
-
- Hasenclever, H. F., M. H. Shacklette, A. W. Hunter, E. George, and J. Schwarz. 1969. The use of cultural and histologic methods for the detection of Histoplasma capsulatum in bats: absence of a cellular response. Am. J. Epidemiol. 90:77-83. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

