Estimation of the initial viral growth rate and basic reproductive number during acute HIV-1 infection
- PMID: 20357090
- PMCID: PMC2876646
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00127-10
Estimation of the initial viral growth rate and basic reproductive number during acute HIV-1 infection
Abstract
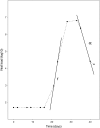
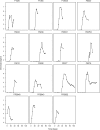
During primary infection, the number of HIV-1 particles in plasma increases rapidly, reaches a peak, and then declines until it reaches a set point level. Understanding the kinetics of primary infection, and its effect on the establishment of chronic infection, is important in defining the early pathogenesis of HIV. We studied the viral dynamics of very early HIV-1 infection in 47 subjects identified through plasma donation screening. We calculated how fast the viral load increases and how variable this parameter is among individuals. We also estimated the basic reproductive ratio, the number of new infected cells generated by an infectious cell at the start of infection when target cells are not limiting. The initial viral doubling time had a median of 0.65 days with an interquartile range of 0.56 to 0.91 days. The median basic reproductive ratio was 8.0 with an interquartile range of 4.9 to 11. In 15 patients, we also observed the postpeak decay of plasma virus and found that the virus decay occurred at a median rate of 0.60 day(-1), corresponding to a half-life of 1.2 days. The median peak viral load was 5.8 log(10) HIV-1 RNA copies/ml, and it was reached 14 days after the virus was quantifiable with an assay, with a lower limit of detection of 50 copies/ml. These results characterize the early plasma viral dynamics in acute HIV infection better than it has been possible thus far. They also better define the challenge that the immune response (or therapeutic intervention) has to overcome to defeat HIV at this early stage.
Figures


References
-
- Abdel-Motal, U. M., J. Gillis, K. Manson, M. Wyand, D. Montefiori, K. Stefano-Cole, R. C. Montelaro, J. D. Altman, and R. P. Johnson. 2005. Kinetics of expansion of SIV Gag-specific CD8+ T lymphocytes following challenge of vaccinated macaques. Virology 333:226-238. - PubMed
-
- Daar, E. S., T. Moudgil, R. D. Meyer, and D. D. Ho. 1991. Transient high levels of viremia in patients with primary human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection. N. Engl. J. Med. 324:961-964. - PubMed
-
- Davenport, M. P., G. T. Belz, and R. M. Ribeiro. 2009. The race between infection and immunity: how do pathogens set the pace? Trends Immunol. 30:61-66. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

