Hepatitis C virus differentially modulates activation of forkhead transcription factors and insulin-induced metabolic gene expression
- PMID: 20357092
- PMCID: PMC2876629
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.02344-09
Hepatitis C virus differentially modulates activation of forkhead transcription factors and insulin-induced metabolic gene expression
Abstract
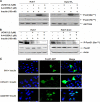
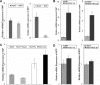
Chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection is often associated with insulin resistance and hepatic steatosis. Insulin regulates gene expression of key enzymes in glucose and lipid metabolism by modulating the activity of specific Forkhead box transcriptional regulators (FoxO1 and FoxA2) via the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)-Akt signaling pathway in the liver. In this study, we observed that HCV infection of human hepatocytes impaired insulin-induced FoxO1 translocation from the nucleus to the cytoplasm and significantly reduced accumulation of FoxA2 in the nucleus. Phosphorylation of FoxO1 at Ser(256), a downstream target for Akt, was inhibited in hepatocytes infected with HCV or expressing the core protein or full-length (FL) genome of HCV. Further, an interaction between FoxO1 and 14-3-3 protein, important for FoxO1 translocation, was inhibited in HCV core-expressing cells. Hepatocytes infected with HCV, expressing the core protein alone or polyprotein displayed an increased level of glucose-6-phosphatase (G6P) mRNA. On the other hand, microsomal triglycerol transfer protein (MTP) activity and apolipoprotein B (ApoB) secretion were significantly reduced in hepatocytes expressing HCV proteins. Together, these observations suggest that HCV infection or ectopic expression of the core protein either alone or together with other viral proteins from an FL gene construct differentially modulates FoxO1 and FoxA2 activation and affects insulin-induced metabolic gene regulation in human hepatocytes.
Figures







References
-
- Adinolfi, L. E., M. Gambardella, A. Andreana, M. F. Tripodi, R. Utili, and G. Ruggiero. 2001. Steatosis accelerates the progression of liver damage of chronic hepatitis C patients and correlates with specific HCV genotype and visceral obesity. Hepatology 33:1358-1364. - PubMed
-
- Altomonte, J., A. Richter, S. Harbaran, J. Suriawinata, J. Nakae, S. N. Thung, M. Meseck, D. Accili, and H. Dong. 2003. Inhibition of Foxo1 function is associated with improved fasting glycemia in diabetic mice. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 285:E718-E728. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

