Ectopic expression of apple F3'H genes contributes to anthocyanin accumulation in the Arabidopsis tt7 mutant grown under nitrogen stress
- PMID: 20357139
- PMCID: PMC2879788
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.109.152801
Ectopic expression of apple F3'H genes contributes to anthocyanin accumulation in the Arabidopsis tt7 mutant grown under nitrogen stress
Abstract
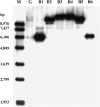
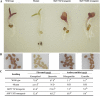
Three genes encoding flavonoid 3'-hydroxylase (F3'H) in apple (Malus x domestica), designated MdF3'HI, MdF3'HIIa, and MdF3'HIIb, have been identified. MdF3'HIIa and MdF3'HIIb are almost identical in amino acid sequences, and they are allelic, whereas MdF3'HI has 91% nucleotide sequence identity in the coding region to both MdF3'HIIa and MdF3'HIIb. MdF3'HI and MdF3'HII genes are mapped onto linkage groups 14 and 6, respectively, of the apple genome. Throughout the development of apple fruit, transcriptional levels of MdF3'H genes along with other anthocyanin biosynthesis genes are higher in the red-skinned cv Red Delicious than that in the yellow-skinned cv Golden Delicious. Moreover, patterns of MdF3'H gene expression correspond to accumulation patterns of flavonoids in apple fruit. These findings suggest that MdF3'H genes are coordinately expressed with other genes in the anthocyanin biosynthetic pathway in apple. The functionality of these apple F3'H genes has been demonstrated via their ectopic expression in both the Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana) transparent testa7-1 (tt7) mutant and tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum). When grown under nitrogen-deficient conditions, transgenic Arabidopsis tt7 seedlings expressing apple F3'H regained red color pigmentation and significantly accumulated both 4'-hydrylated pelargonidin and 3',4'-hydrylated cyanidin. When compared with wild-type plants, flowers of transgenic tobacco lines overexpressing apple F3'H genes exhibited enhanced red color pigmentation. This suggests that the F3'H enzyme may coordinately interact with other flavonoid enzymes in the anthocyanin biosynthesis pathway.
Figures







References
-
- Aharoni A, De Vos CH, Wein M, Sun Z, Greco R, Kroon A, Mol JN, O'Connell AP. (2001) The strawberry FaMYB1 transcription factor suppresses anthocyanin and flavonol accumulation in transgenic tobacco. Plant J 28: 319–332 - PubMed
-
- Brugliera F, Barri-Rewell G, Holton TA, Mason JG. (1999) Isolation and characterization of a flavonoid 3′-hydroxylase cDNA clone corresponding to the Ht1 locus of Petunia hybrida. Plant J 19: 441–451 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

