Cyclin-dependent kinase 5 modulates the transcriptional activity of the mineralocorticoid receptor and regulates expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor
- PMID: 20357208
- PMCID: PMC2870940
- DOI: 10.1210/me.2009-0395
Cyclin-dependent kinase 5 modulates the transcriptional activity of the mineralocorticoid receptor and regulates expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor
Abstract
Glucocorticoids, major end effectors of the stress response, play an essential role in the homeostasis of the central nervous system (CNS) and contribute to memory consolidation and emotional control through their intracellular receptors, the glucocorticoid and mineralocorticoid receptors. Cyclin-dependent kinase 5 (CDK5), on the other hand, plays important roles in the morphogenesis and functions of the central nervous system, and its aberrant activation has been associated with development of neurodegenerative disorders. We previously reported that CDK5 phosphorylated the glucocorticoid receptor and modulated its transcriptional activity. Here we found that CDK5 also regulated mineralocorticoid receptor-induced transcriptional activity by phosphorylating multiple serine and threonine residues located in its N-terminal domain through physical interaction. Aldosterone and dexamethasone, respectively, increased and suppressed mRNA/protein expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) in rat cortical neuronal cells, whereas the endogenous glucocorticoid corticosterone showed a biphasic effect. CDK5 enhanced the effect of aldosterone and dexamethasone on BDNF expression. Because this neurotrophic factor plays critical roles in neuronal viability, synaptic plasticity, consolidation of memory, and emotional changes, we suggest that aberrant activation of CDK5 might influence these functions through corticosteroid receptors/BDNF.
Figures

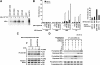



Similar articles
-
Cyclin-dependent kinase 5 differentially regulates the transcriptional activity of the glucocorticoid receptor through phosphorylation: clinical implications for the nervous system response to glucocorticoids and stress.Mol Endocrinol. 2007 Jul;21(7):1552-68. doi: 10.1210/me.2006-0345. Epub 2007 Apr 17. Mol Endocrinol. 2007. PMID: 17440046
-
The BDNF/TrkB signaling pathway is involved in heat hyperalgesia mediated by Cdk5 in rats.PLoS One. 2014 Jan 21;9(1):e85536. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0085536. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24465591 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of aberrant cyclin-dependent kinase 5 activity attenuates isoflurane neurotoxicity in the developing brain.Neuropharmacology. 2014 Feb;77:90-9. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2013.09.006. Epub 2013 Sep 18. Neuropharmacology. 2014. PMID: 24055498
-
Corticosterone effects on BDNF expression in the hippocampus. Implications for memory formation.Stress. 2000 May;3(3):201-8. doi: 10.3109/10253890009001124. Stress. 2000. PMID: 10938581 Review.
-
Evolution of hormone selectivity in glucocorticoid and mineralocorticoid receptors.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2013 Sep;137:57-70. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2013.07.009. Epub 2013 Jul 29. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 23907018 Review.
Cited by
-
Posttranslational Modifications of the Mineralocorticoid Receptor and Cardiovascular Aging.Front Mol Biosci. 2021 May 28;8:667990. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.667990. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Biosci. 2021. PMID: 34124152 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Context-dependent mechanisms modulating aldosterone signaling in the kidney.Clin Exp Nephrol. 2016 Oct;20(5):663-670. doi: 10.1007/s10157-016-1232-5. Epub 2016 Feb 5. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2016. PMID: 26846783 Review.
-
A Shorter-Bout of HIIT Is More Effective to Promote Serum BDNF and VEGF-A Levels and Improve Cognitive Function in Healthy Young Men.Front Physiol. 2022 Jun 29;13:898603. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.898603. eCollection 2022. Front Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35846013 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of CDK5 in Tumours and Tumour Microenvironments.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Dec 31;13(1):101. doi: 10.3390/cancers13010101. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33396266 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Coping with unpredictability: dopaminergic and neurotrophic responses to omission of expected reward in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.).PLoS One. 2014 Jan 17;9(1):e85543. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0085543. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24465595 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kino T, Chrousos GP 2005 Glucocorticoid effect on gene expression. In: Steckler T, Kalin NH, Reul JMHM, eds. Handbook on stress and the brain. Amsterdam: Elsevier BV; 295–312
-
- de Kloet ER, Derijk RH, Meijer OC 2007 Therapy insight: is there an imbalanced response of mineralocorticoid and glucocorticoid receptors in depression? Nat Clin Pract Endocrinol Metab 3:168–179 - PubMed
-
- Fietta P, Fietta P 2007 Glucocorticoids and brain functions. Riv Biol 100:403–418 - PubMed
-
- Rashid S, Lewis GF 2005 The mechanisms of differential glucocorticoid and mineralocorticoid action in the brain and peripheral tissues. Clin Biochem 38:401–409 - PubMed
-
- Kino T, Chrousos GP 2004 Glucocorticoid and mineralocorticoid receptors and associated diseases. Essays Biochem 40:137–155 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

