New therapeutic and biomarker discovery for peripheral diabetic neuropathy: PARP inhibitor, nitrotyrosine, and tumor necrosis factor-{alpha}
- PMID: 20357221
- PMCID: PMC2875829
- DOI: 10.1210/en.2009-1342
New therapeutic and biomarker discovery for peripheral diabetic neuropathy: PARP inhibitor, nitrotyrosine, and tumor necrosis factor-{alpha}
Abstract
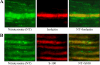
This study evaluated poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) inhibition as a new therapeutic approach for peripheral diabetic neuropathy using clinically relevant animal model and endpoints, and nitrotyrosine (NT), TNF-alpha, and nitrite/nitrate as potential biomarkers of the disease. Control and streptozotocin-diabetic rats were maintained with or without treatment with orally active PARP inhibitor 10-(4-methyl-piperazin-1-ylmethyl)-2H-7-oxa-1,2-diaza-benzo[de]anthracen-3-one (GPI-15,427), 30 mg kg(-1) d(-1), for 10 wk after first 2 wk without treatment. Therapeutic efficacy was evaluated by poly(ADP-ribosyl)ated protein expression (Western blot analysis), motor and sensory nerve conduction velocities, and tibial nerve morphometry. Sciatic nerve and spinal cord NT, TNF-alpha, and nitrite/nitrate concentrations were measured by ELISA. NT localization in peripheral nervous system was evaluated by double-label fluorescent immunohistochemistry. A PARP inhibitor treatment counteracted diabetes-induced motor and sensory nerve conduction slowing, axonal atrophy of large myelinated fibers, and increase in sciatic nerve and spinal cord NT and TNF-alpha concentrations. Sciatic nerve NT and TNF-alpha concentrations inversely correlated with motor and sensory nerve conduction velocities and myelin thickness, whereas nitrite/nitrate concentrations were indistinguishable between control and diabetic groups. NT accumulation was identified in endothelial and Schwann cells of the peripheral nerve, neurons, astrocytes, and oligodendrocytes of the spinal cord, and neurons and glial cells of the dorsal root ganglia. The findings identify PARP as a compelling drug target for prevention and treatment of both functional and structural manifestations of peripheral diabetic neuropathy and provide rationale for detailed evaluation of NT and TNF-alpha as potential biomarkers of its presence, severity, and progression.
Figures




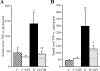
Similar articles
-
Poly(Adenosine 5'-diphosphate-ribose) polymerase inhibition counteracts multiple manifestations of experimental type 1 diabetic nephropathy.Endocrinology. 2009 Dec;150(12):5273-83. doi: 10.1210/en.2009-0628. Epub 2009 Oct 23. Endocrinology. 2009. PMID: 19854869 Free PMC article.
-
Poly(ADP-ribose)polymerase inhibition counteracts renal hypertrophy and multiple manifestations of peripheral neuropathy in diabetic Akita mice.Int J Mol Med. 2011 Oct;28(4):629-35. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2011.709. Epub 2011 May 23. Int J Mol Med. 2011. PMID: 21617845 Free PMC article.
-
Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) inhibition counteracts multiple manifestations of kidney disease in long-term streptozotocin-diabetic rat model.Biochem Pharmacol. 2010 Apr 1;79(7):1007-14. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2009.11.018. Epub 2009 Nov 27. Biochem Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 19945439 Free PMC article.
-
Role for poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase activation in diabetic nephropathy, neuropathy and retinopathy.Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2005 Jul;3(3):267-83. doi: 10.2174/1570161054368634. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2005. PMID: 16026323 Review.
-
Update on the pathogenesis of diabetic neuropathy.Curr Diab Rep. 2003 Dec;3(6):439-45. doi: 10.1007/s11892-003-0005-1. Curr Diab Rep. 2003. PMID: 14611738 Review.
Cited by
-
Different roles of 12/15-lipoxygenase in diabetic large and small fiber peripheral and autonomic neuropathies.Am J Pathol. 2010 Sep;177(3):1436-47. doi: 10.2353/ajpath.2010.100178. Epub 2010 Aug 19. Am J Pathol. 2010. PMID: 20724598 Free PMC article.
-
Advances About Immunoinflammatory Pathogenesis and Treatment in Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Oct 4;12:748193. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.748193. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34671261 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cardiovascular autonomic neuropathies as complications of diabetes mellitus.Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2012 Feb 28;8(7):405-16. doi: 10.1038/nrendo.2012.21. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2012. PMID: 22371159 Review.
-
Pathogenesis of diabetic neuropathy: bad to the bone.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2011 Dec;1240:70-6. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2011.06309.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2011. PMID: 22172042 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase: An Overview of Mechanistic Approaches and Therapeutic Opportunities in the Management of Stroke.Neurochem Res. 2022 Jul;47(7):1830-1852. doi: 10.1007/s11064-022-03595-z. Epub 2022 Apr 18. Neurochem Res. 2022. PMID: 35437712 Review.
References
-
- Boulton AJ, Vinik AI, Arezzo JC, Bril V, Feldman EL, Freeman R, Malik RA, Maser RE, Sosenko JM, Ziegler D; American Diabetes Association 2005 Diabetic neuropathies: a statement by the American Diabetes Association. Diabetes Care 28:956–962 - PubMed
-
- Veves A, Backonja M, Malik RA 2008 Painful diabetic neuropathy: epidemiology, natural history, early diagnosis, and treatment options. Pain Med 9:660–674 - PubMed
-
- Jagtap P, Szabó C 2005 Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase and the therapeutic effects of its inhibitors. Nat Rev Drug Discov 4:421–440 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

