B cells have distinct roles in host protection against different nematode parasites
- PMID: 20357259
- PMCID: PMC3729113
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.0902879
B cells have distinct roles in host protection against different nematode parasites
Abstract
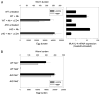
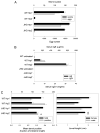
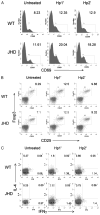
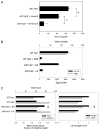
B cells can mediate protective responses against nematode parasites by supporting Th2 cell development and/or by producing Abs. To examine this, B cell-deficient mice were inoculated with Nippostrongylus brasiliensis or Heligmosomoides polygyrus. B cell-deficient and wild type mice showed similar elevations in Th2 cytokines and worm expulsion after N. brasiliensis inoculation. Worm expulsion was inhibited in H. polygyrus-inoculated B cell-deficient mice, although Th2 cytokine elevations in mucosal tissues were unaffected. Impaired larval migration and development was compromised as early as day 4 after H. polygyrus challenge, and administration of immune serum restored protective immunity in B cell-deficient mice, indicating a primary role for Ab. Immune serum even mediated protective effects when administered to naive mice prior to inoculation. This study suggests variability in the importance of B cells in mediating protection against intestinal nematode parasites, and it indicates an important role for Ab in resistance to tissue-dwelling parasites.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Diemert DJ, Bethony JM, Hotez PJ. Hookworm vaccines. Clin Infect Dis. 2008;46:282–288. - PubMed
-
- Scales HE, Ierna MX, Lawrence CE. The role of IL-4, IL-13 and IL-4Ralpha in the development of protective and pathological responses to Trichinella spiralis. Parasite Immunol. 2007;29:81–91. - PubMed
-
- Finkelman FD, Shea-Donohue T, Morris SC, Gildea L, Strait R, Madden KB, Schopf L, Urban JF., Jr Interleukin-4- and interleukin-13-mediated host protection against intestinal nematode parasites. Immunol Rev. 2004;201:139–155. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

