TLR4 is a negative regulator in noninfectious lung inflammation
- PMID: 20357263
- PMCID: PMC10733842
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1000009
TLR4 is a negative regulator in noninfectious lung inflammation
Abstract
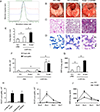
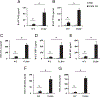
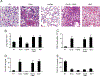
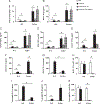
Low m.w. hyaluronan (LMW HA) has been shown to elicit the expression of proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines in various cells in vitro. However, the effects of this molecule in vivo are unknown. In this study, we report that intratracheal administration of LMW HA (200 kDa) causes inflammation in mouse lung. A lack of TLR4 is associated with even stronger inflammatory response in the lung as shown by increased neutrophil counts and elevated cytokine and chemokine concentrations. We also demonstrate that TLR4 anti-inflammatory signaling is dependent upon a MyD88-independent pathway. TLR4-mediated IL-1R antagonist production plays a negative regulatory role in LMW HA (200 kDa) induced lung inflammation. These data provide a molecular level explanation for the function of TLR4 in LMW HA (200 kDa)-induced lung inflammation, as inhibition of the beta form of pro-IL-1 promotes an anti-inflammatory response.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures
The authors have no financial conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
TLR4 through IFN-β promotes low molecular mass hyaluronan-induced neutrophil apoptosis.J Immunol. 2011 Jan 1;186(1):556-62. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1001630. Epub 2010 Nov 22. J Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21098223
-
Plasminogen activator inhibitor type-1 deficiency exaggerates LPS-induced acute lung injury through enhancing Toll-like receptor 4 signaling pathway.Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 2011 Sep;22(6):480-6. doi: 10.1097/MBC.0b013e328346ef56. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 2011. PMID: 21577093
-
Hyaluronan ameliorates LPS-induced acute lung injury in mice via Toll-like receptor (TLR) 4-dependent signaling pathways.Int Immunopharmacol. 2015 Oct;28(2):1050-8. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2015.08.021. Epub 2015 Aug 28. Int Immunopharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26321117
-
TLR4 is necessary for hyaluronan-mediated airway hyperresponsiveness after ozone inhalation.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2010 Apr 1;181(7):666-75. doi: 10.1164/rccm.200903-0381OC. Epub 2009 Dec 10. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2010. PMID: 20007931 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of non-infectious lung injury, inflammation, and repair by the extracellular matrix glycosaminoglycan hyaluronan.Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2010 Jun;293(6):982-5. doi: 10.1002/ar.21102. Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2010. PMID: 20186964 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Hyaluronan signaling during ozone-induced lung injury requires TLR4, MyD88, and TIRAP.PLoS One. 2011;6(11):e27137. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0027137. Epub 2011 Nov 4. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 22073274 Free PMC article.
-
An endothelial TLR4-VEGFR2 pathway mediates lung protection against oxidant-induced injury.FASEB J. 2016 Mar;30(3):1317-27. doi: 10.1096/fj.15-275024. Epub 2015 Dec 11. FASEB J. 2016. PMID: 26655705 Free PMC article.
-
Receptor for advanced glycation endproducts (RAGE) maintains pulmonary structure and regulates the response to cigarette smoke.PLoS One. 2017 Jul 5;12(7):e0180092. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0180092. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28678851 Free PMC article.
-
Low molecular weight hyaluronan activates cytosolic phospholipase A2α and eicosanoid production in monocytes and macrophages.J Biol Chem. 2014 Feb 14;289(7):4470-88. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.515106. Epub 2013 Dec 23. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24366870 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Toll-like Receptor 4 Deficiency Aggravates Airway Hyperresponsiveness and Inflammation by Impairing Neutrophil Apoptosis in a Toluene Diisocyanate-Induced Murine Asthma Model.Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2020 Jul;12(4):608-625. doi: 10.4168/aair.2020.12.4.608. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2020. PMID: 32400128 Free PMC article.
References
-
- O’Neill LA 2008. The interleukin-1 receptor/Toll-like receptor superfamily: 10 years of progress. Immunol. Rev. 226: 10–18. - PubMed
-
- Miyake K 2007. Innate immune sensing of pathogens and danger signals by cell surface Toll-like receptors. Semin. Immunol. 19: 3–10. - PubMed
-
- Taylor KR, Trowbridge JM, Rudisill JA, Termeer CC, Simon JC, and Gallo RL. 2004. Hyaluronan fragments stimulate endothelial recognition of injury through TLR4. J. Biol. Chem. 279: 17079–17084. - PubMed
-
- Akira S, Uematsu S, and Takeuchi O. 2006. Pathogen recognition and innate immunity. Cell 124: 783–801. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

