First come, first served revisited: factors affecting the same alternative splicing event have different effects on the relative rates of intron removal
- PMID: 20357345
- PMCID: PMC2856885
- DOI: 10.1261/rna.1993510
First come, first served revisited: factors affecting the same alternative splicing event have different effects on the relative rates of intron removal
Abstract
Alternative splicing accounts for much of the complexity in higher eukaryotes. Thus, its regulation must allow for flexibility without hampering either its specificity or its fidelity. The mechanisms involved in alternative splicing regulation, especially those acting through coupling with transcription, have not been deeply studied in in vivo models. Much of our knowledge comes from in vitro approaches, where conditions can be precisely controlled at the expense of losing several levels of regulation present in intact cells. Here we studied the relative order of removal of the introns flanking a model alternative cassette exon. We show that there is a preferential removal of the intron downstream from the cassette exon before the upstream intron has been removed. Most importantly, both cis-acting mutations and trans-acting factors that regulate the model alternative splicing event differentially affect the relative order of removal. However, reduction of transcriptional elongation causing higher inclusion of the cassette exon does not change the order of intron removal, suggesting that the assumption, according to the "first come, first served" model, that slow elongation promotes preferential excision of the upstream intron has to be revised. We propose instead that slow elongation favors commitment to exon inclusion during spliceosome assembly. Our results reveal that measuring the order of intron removal may be a straightforward read-out to discriminate among different mechanisms of alternative splice site selection.
Figures
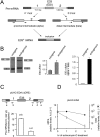
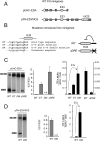
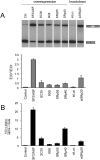
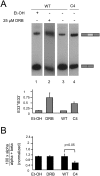

References
-
- Aebi M, Weissmann C 1987. Precision and orderliness in splicing. Trends Genet 4: 102–107
-
- Beyer AL, Osheim YN 1988. Splice site selection, rate of splicing, and alternative splicing on nascent transcripts. Genes & Dev 2: 754–765 - PubMed
-
- Cramer P, Caceres JF, Cazalla D, Kadener S, Muro AF, Baralle FE, Kornblihtt AR 1999. Coupling of transcription with alternative splicing: RNA pol II promoters modulate SF2/ASF and 9G8 effects on an exonic splicing enhancer. Mol Cell 4: 251–258 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
