Fibroblast growth factor 21 action in the brain increases energy expenditure and insulin sensitivity in obese rats
- PMID: 20357365
- PMCID: PMC2889784
- DOI: 10.2337/db09-1878
Fibroblast growth factor 21 action in the brain increases energy expenditure and insulin sensitivity in obese rats
Abstract
Objective: The hormone fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) exerts diverse, beneficial effects on energy balance and insulin sensitivity when administered systemically to rodents with diet-induced obesity (DIO). The current studies investigate whether central FGF21 treatment recapitulates these effects.
Research design and methods: After preliminary dose-finding studies, either saline vehicle or recombinant human FGF21 (0.4 microg/day) was infused continuously for 2 weeks into the lateral cerebral ventricle of male Wistar rats rendered obese by high-fat feeding. Study end points included measures of energy balance (body weight, body composition, food intake, energy expenditure, and circulating and hepatic lipids) and glucose metabolism (insulin tolerance test, euglycemic-hyperinsulinemic clamp, and hepatic expression of genes involved in glucose metabolism).
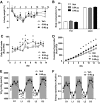
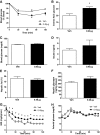
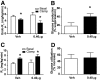
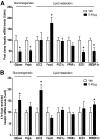
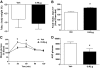
Results: Compared with vehicle, continuous intracerebroventricular infusion of FGF21 increased both food intake and energy expenditure in rats with DIO, such that neither body weight nor body composition was altered. Despite unchanged body fat content, rats treated with intracerebroventricular FGF21 displayed a robust increase of insulin sensitivity due to increased insulin-induced suppression of both hepatic glucose production and gluconeogenic gene expression, with no change of glucose utilization.
Conclusions: FGF21 action in the brain increases hepatic insulin sensitivity and metabolic rate in rats with DIO. These findings identify the central nervous system as a potentially important target for the beneficial effects of FGF21 in the treatment of diabetes and obesity.
Figures
References
-
- Coskun T, Bina HA, Schneider MA, Dunbar JD, Hu CC, Chen Y, Moller DE, Kharitonenkov A: Fibroblast growth factor 21 corrects obesity in mice. Endocrinology 2008;149:6018–6027 - PubMed
-
- Xu J, Lloyd DJ, Hale C, Stanislaus S, Chen M, Sivits G, Vonderfecht S, Hecht R, Li YS, Lindberg RA, Chen JL, Jung DY, Zhang Z, Ko HJ, Kim JK, Véniant MM: Fibroblast growth factor 21 reverses hepatic steatosis, increases energy expenditure, and improves insulin sensitivity in diet-induced obese mice. Diabetes 2009;58:250–259 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U24 DK076126/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK090320/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK-083042/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- F32-DK-080604-01/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK083042/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK-068384/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK035816/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- F32 DK080604/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U24-DK-076126/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK052989/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK-052989/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK-035816/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P01 DK068384/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

