Effectiveness of removable walker cast versus nonremovable fiberglass off-bearing cast in the healing of diabetic plantar foot ulcer: a randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 20357377
- PMCID: PMC2890332
- DOI: 10.2337/dc09-1708
Effectiveness of removable walker cast versus nonremovable fiberglass off-bearing cast in the healing of diabetic plantar foot ulcer: a randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the efficacy of a removable cast walker compared with that of a nonremovable fiberglass off-bearing cast in the treatment of diabetic plantar foot ulcer.
Research design and methods: Forty-five adult diabetic patients with nonischemic, noninfected neuropathic plantar ulcer were randomly assigned for treatment with a nonremovable fiberglass off-bearing cast (total contact cast [TCC] group) or walker cast (Stabil-D group). Treatment duration was 90 days. Percent reduction in ulcer surface area and total healing rates were evaluated after treatment.
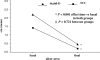
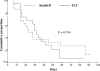
Results: A total of 48 patients were screened; however, 2 patients in the TCC group and 1 patient in the Stabil-D group did not complete the study and were considered dropouts. There were no significant differences in demographic and clinic characteristics of the 45 patients completing the study. Ulcer surface decreased from 1.41 to 0.21 cm(2) (P < 0.001) in the TCC group and from 2.18 to 0.45 cm(2) (P < 0.001) in the Stabil-D group, with no significant differences between groups (P = 0.722). Seventeen patients (73.9%) in the TCC group and 16 patients (72.7%) in the Stabil-D group achieved healing (P = 0.794). Average healing time was 35.3 +/- 3.1 and 39.7 +/- 4.2 days in the TCC and Stabil-D group, respectively (P = 0.708).
Conclusions: The Stabil-D cast walker, although removable, was equivalent in efficacy to the TCC in terms of ulcer size reduction and total healing rate. The easier use of Stabil-D may help increase the use of off-loading devices in the management of plantar neuropathic diabetic foot ulcers.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT01005264.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effectiveness and safety of a nonremovable fiberglass off-bearing cast versus a therapeutic shoe in the treatment of neuropathic foot ulcers: a randomized study.Diabetes Care. 2000 Dec;23(12):1746-51. doi: 10.2337/diacare.23.12.1746. Diabetes Care. 2000. PMID: 11128345 Clinical Trial.
-
Nonremovable, windowed, fiberglass cast boot in the treatment of diabetic plantar ulcers: efficacy, safety, and compliance.Diabetes Care. 2003 Oct;26(10):2848-52. doi: 10.2337/diacare.26.10.2848. Diabetes Care. 2003. PMID: 14514590 Clinical Trial.
-
Offloading systems for the treatment of neuropathic foot ulcers in patients with diabetes mellitus: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials for the development of the Italian guidelines for the treatment of diabetic foot syndrome.Acta Diabetol. 2024 Jun;61(6):693-703. doi: 10.1007/s00592-024-02262-9. Epub 2024 Mar 15. Acta Diabetol. 2024. PMID: 38489054 Review.
-
A randomized trial of two irremovable off-loading devices in the management of plantar neuropathic diabetic foot ulcers.Diabetes Care. 2005 Mar;28(3):555-9. doi: 10.2337/diacare.28.3.555. Diabetes Care. 2005. PMID: 15735187 Clinical Trial.
-
Off-loading the diabetic foot for ulcer prevention and healing.J Vasc Surg. 2010 Sep;52(3 Suppl):37S-43S. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2010.06.007. J Vasc Surg. 2010. PMID: 20804932 Review.
Cited by
-
Effectiveness of offloading interventions to heal foot ulcers in persons with diabetes: a systematic review.Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2020 Mar;36 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):e3275. doi: 10.1002/dmrr.3275. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2020. PMID: 32176438 Free PMC article.
-
Randomised clinical trial to compare total contact casts, healing sandals and a shear-reducing removable boot to heal diabetic foot ulcers.Int Wound J. 2015 Dec;12(6):710-5. doi: 10.1111/iwj.12213. Epub 2014 Feb 21. Int Wound J. 2015. PMID: 24618113 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Treatment of Charcot Neuroarthropathy and osteomyelitis of the same foot: a retrospective cohort study.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2017 Nov 16;18(1):460. doi: 10.1186/s12891-017-1818-4. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2017. PMID: 29145857 Free PMC article.
-
Total contact cast wall load in patients with a plantar forefoot ulcer and diabetes.J Foot Ankle Res. 2016 Jan 7;9:2. doi: 10.1186/s13047-015-0119-0. eCollection 2016. J Foot Ankle Res. 2016. PMID: 26744604 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of a new versus standard removable offloading device in patients with neuropathic diabetic foot ulcers: a French national, multicentre, open-label randomized, controlled trial.BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care. 2020 May;8(1):e000954. doi: 10.1136/bmjdrc-2019-000954. BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care. 2020. PMID: 32393479 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Boulton AJ: The diabetic foot: from art to science: the 18th Camillo Golgi Lecture. Diabetologia 2004; 47: 1343–1353 - PubMed
-
- Frykberg RG, Lavery LA, Pham H, Harvey C, Harkless L, Veves A: Role of neuropathy and high foot pressures in diabetic foot ulceration. Diabetes Care 1998; 21: 1714–1719 - PubMed
-
- Rathur HM, Boulton AJ: Pathogenesis of foot ulcers and the need for offloading. Horm Metab Res 2005; 37(Suppl 1): 61–68 - PubMed
-
- Boulton AJ, Bowker JH, Gadia M, Lemerman R, Caswell K, Skyler JS, Sosenko JM: Use of plaster casts in the management of diabetic neuropathic foot ulcers. Diabetes Care 1986; 9: 149–152 - PubMed
-
- Brem H, Sheehan P, Boulton AJ: Protocol for treatment of diabetic foot ulcers. Am J Surg 2004; 187: S1–S10 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

